-
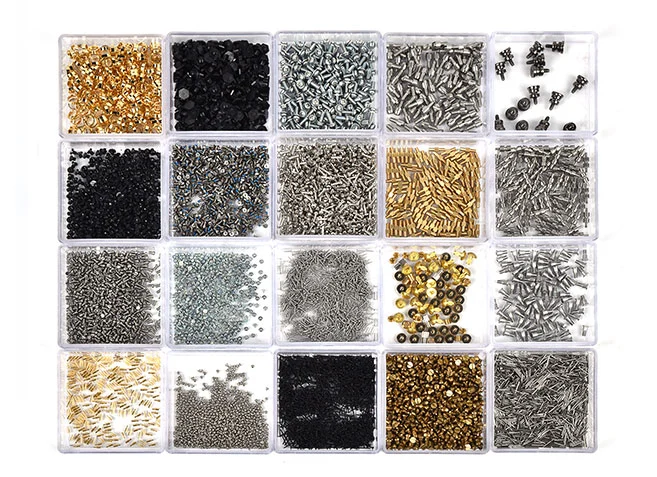 Micro Screws
Micro Screws
-
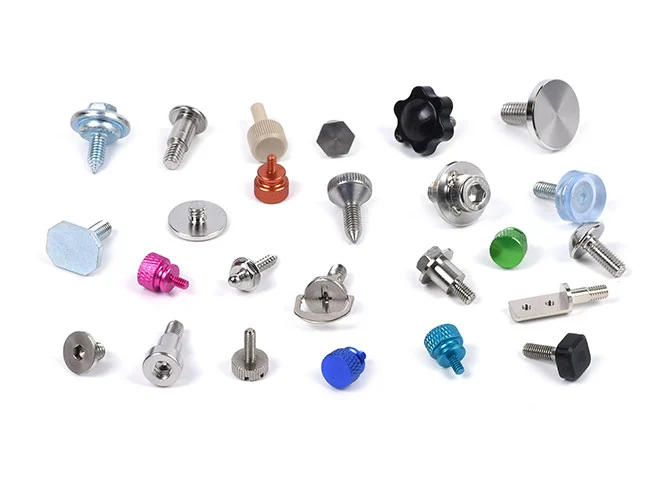 Big Head Screws
Big Head Screws
-
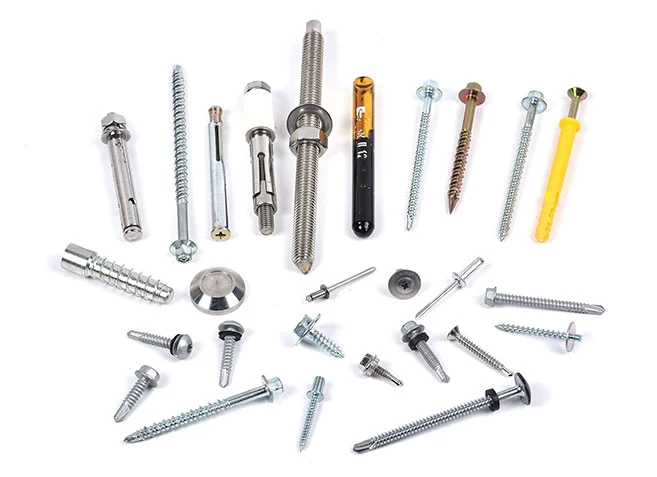 Construction Screws
Construction Screws
-
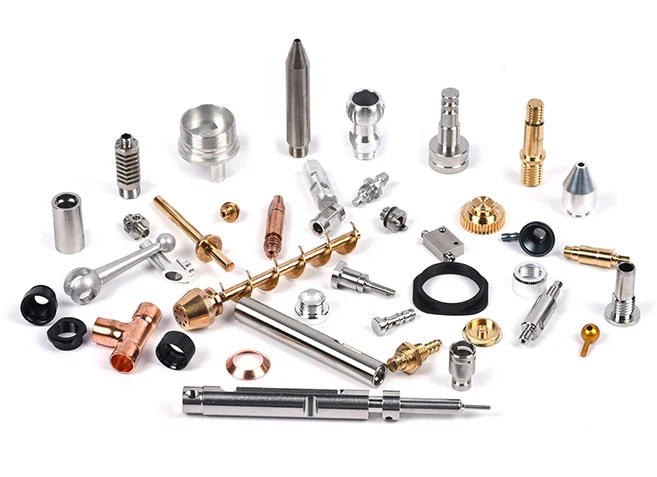 CNC Lathe Machining Parts
CNC Lathe Machining Parts
-
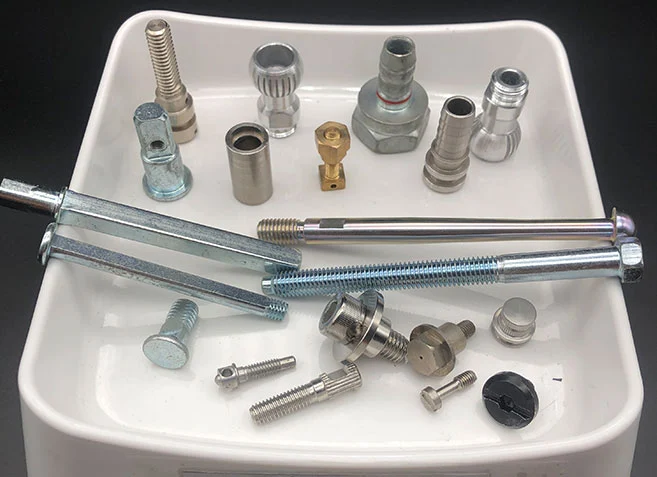 Cold Forged and Undergo Secondary Processing Products
Cold Forged and Undergo Secondary Processing Products
-
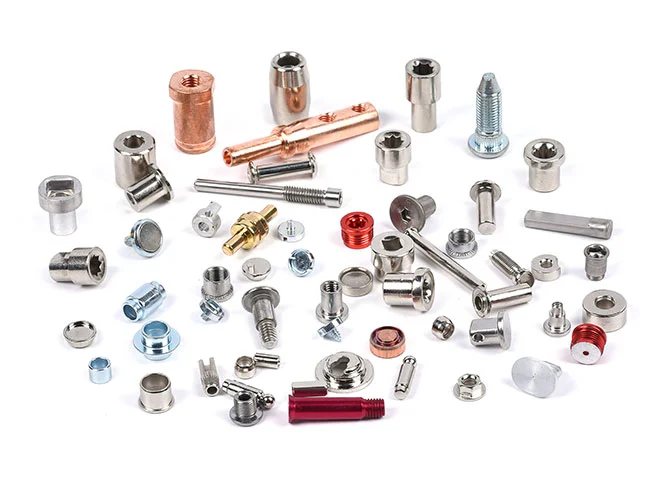 Multi Station Cold Heading Screws
Multi Station Cold Heading Screws
-
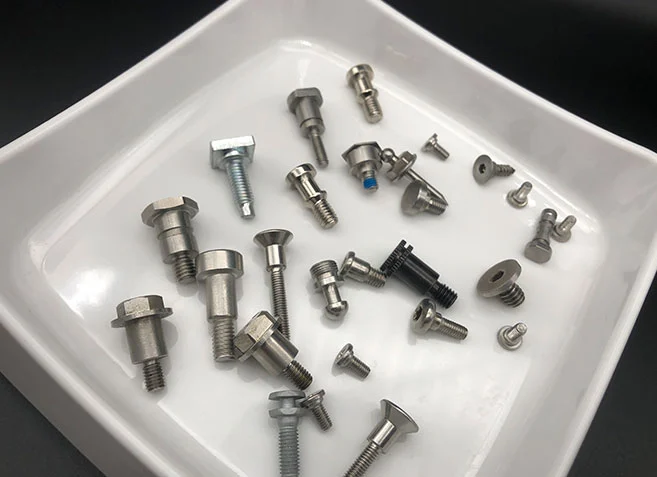 Step Screw
Step Screw
-
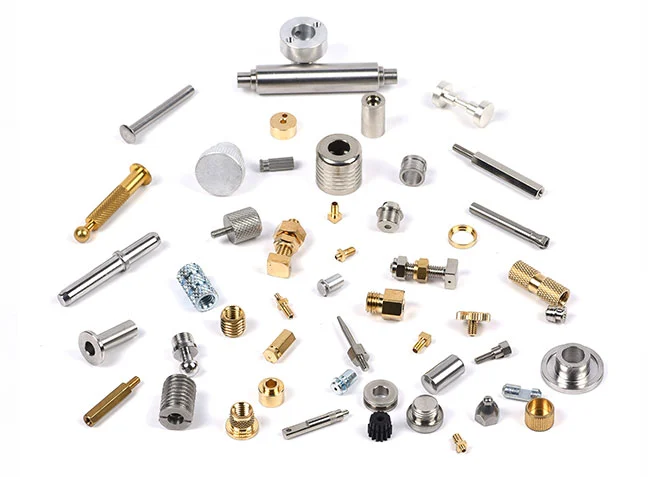 Automatic Lathe Machining Parts
Automatic Lathe Machining Parts
-
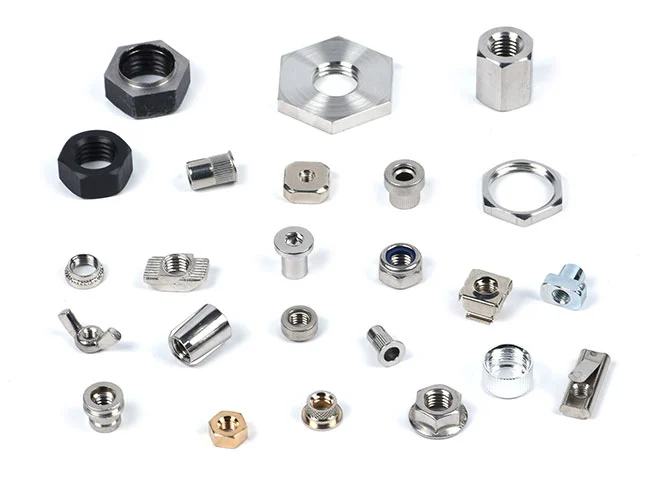 High Difficulty Challenge Cold Heading Fasteners
High Difficulty Challenge Cold Heading Fasteners
-
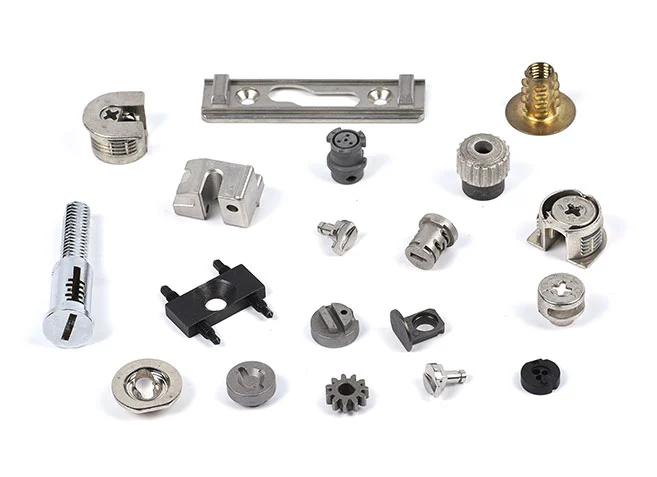 New Tech Fasteners
New Tech Fasteners
-
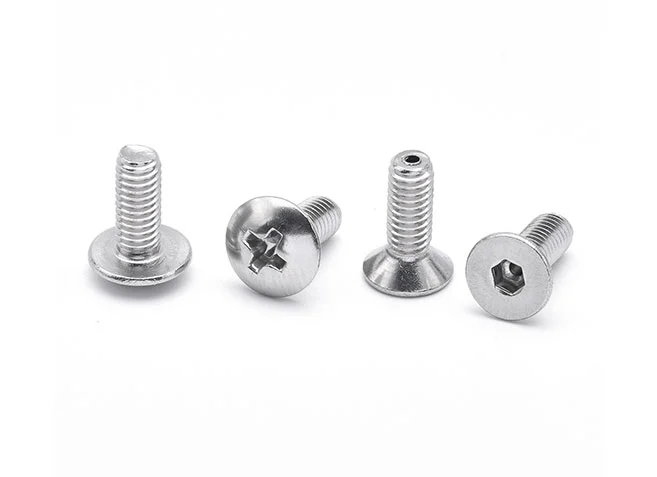 Machine Screws
Machine Screws
-
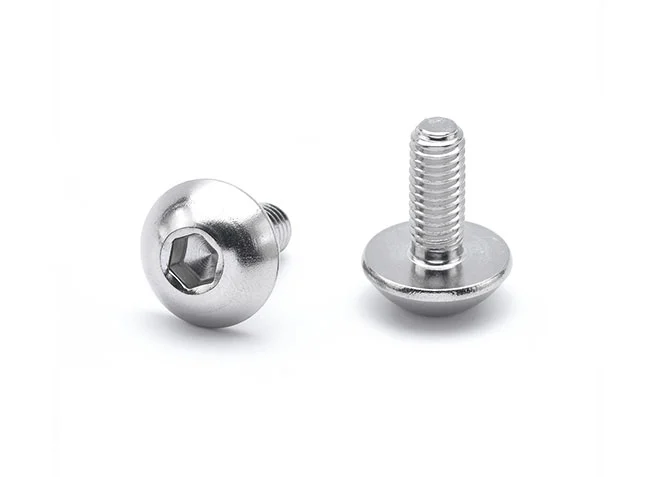 Socket Cap Screws
Socket Cap Screws
-
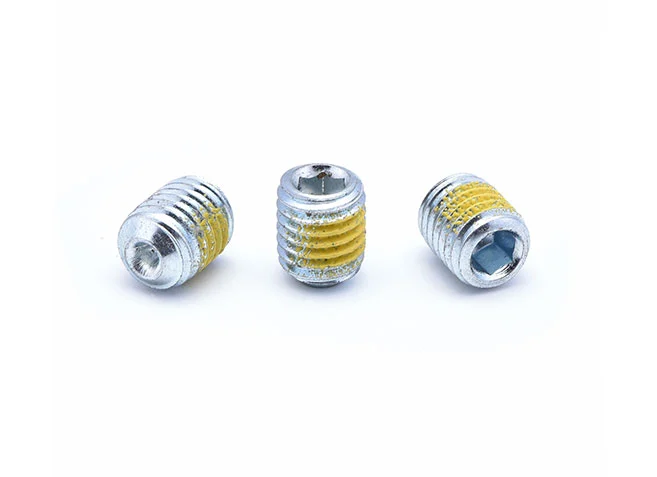 Hexagon Socket Set Screws
Hexagon Socket Set Screws
-
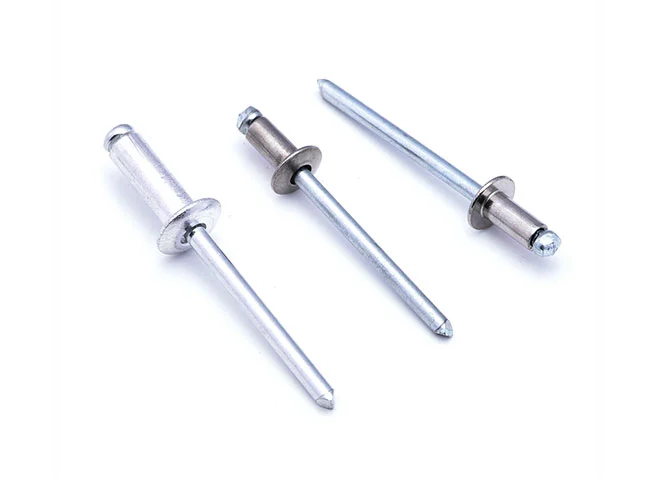 Pull Out Rivet
Pull Out Rivet
-
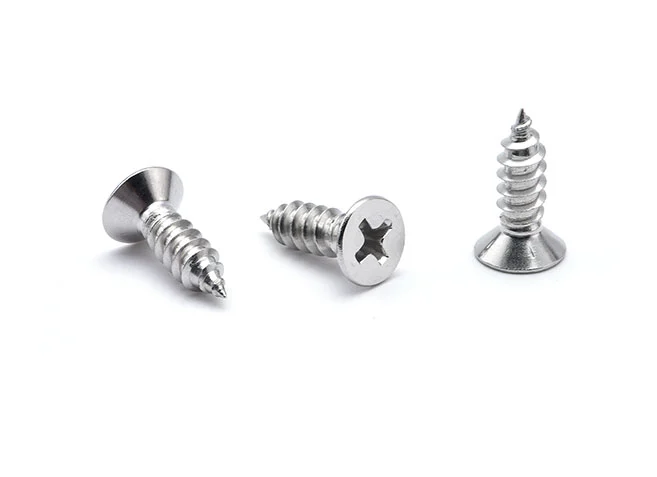 Self Tapping Screws
Self Tapping Screws
-
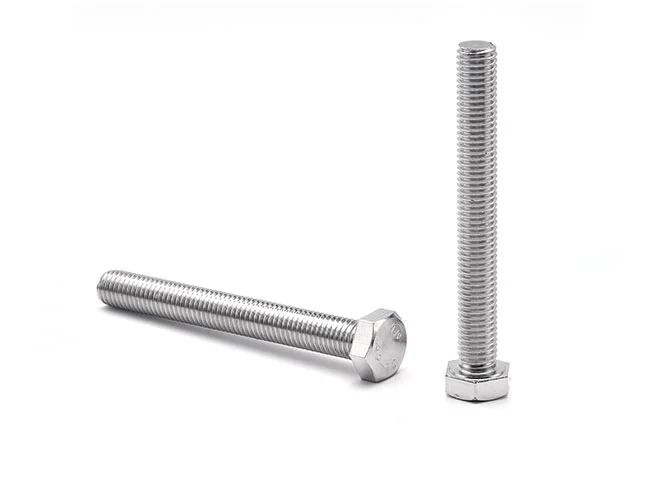 Hex Bolts
Hex Bolts
-
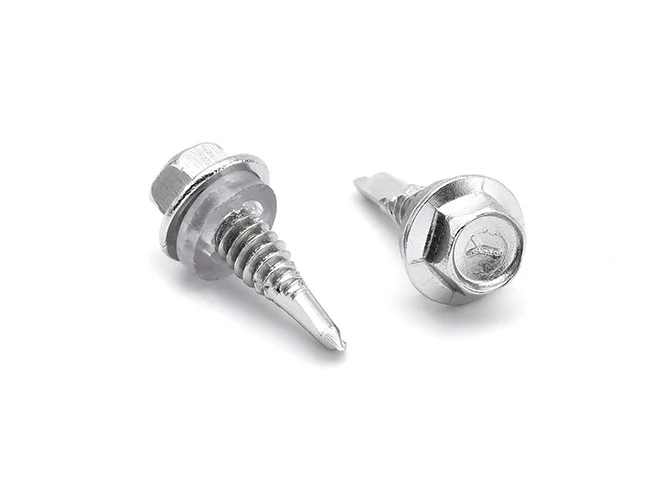 Self Drilling Screws
Self Drilling Screws
-
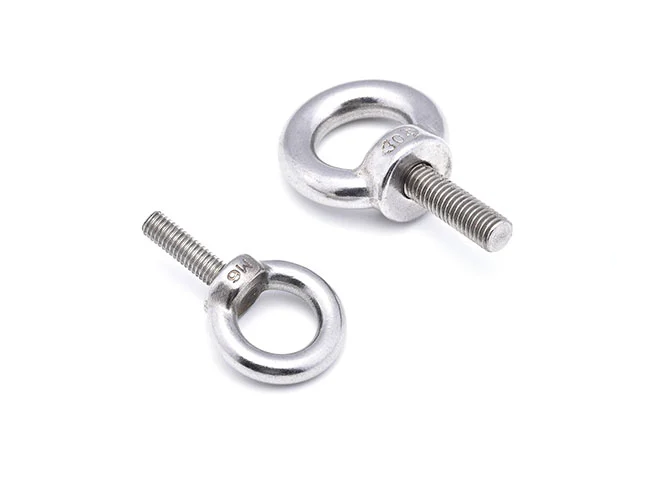 Eye Bolts
Eye Bolts
-
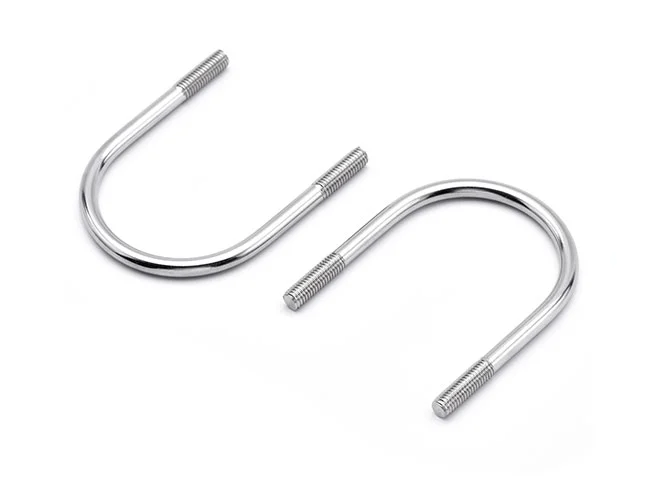 U-bolts
U-bolts
-
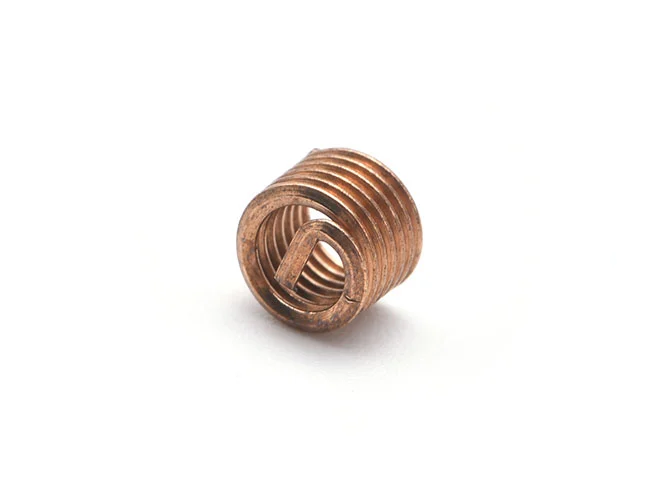 Threaded Sheath
Threaded Sheath
-
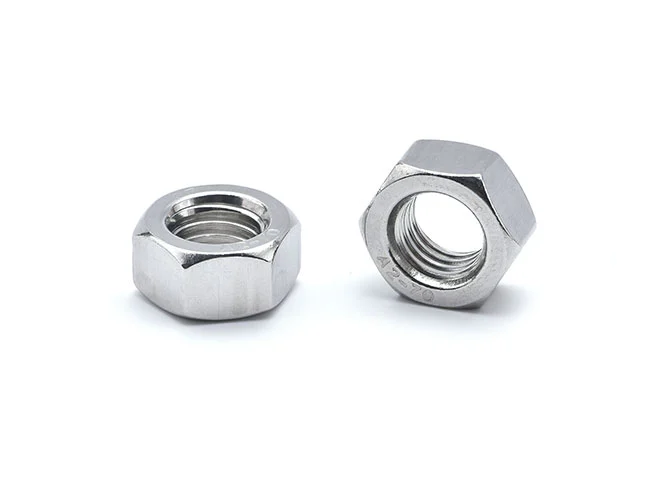 Hex Nut
Hex Nut
-
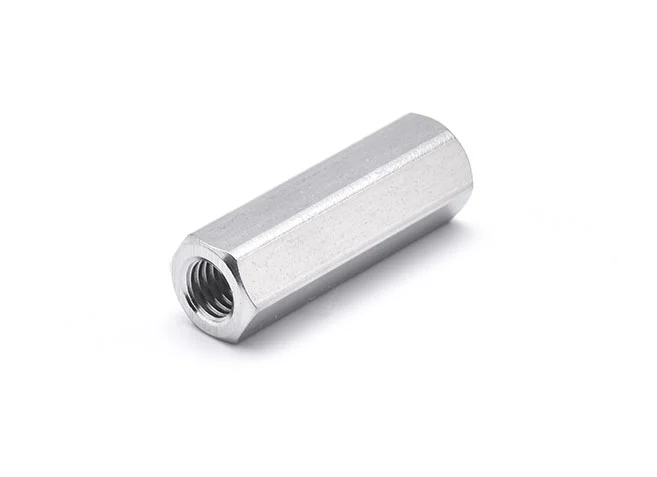 Hex Long Nut
Hex Long Nut
-
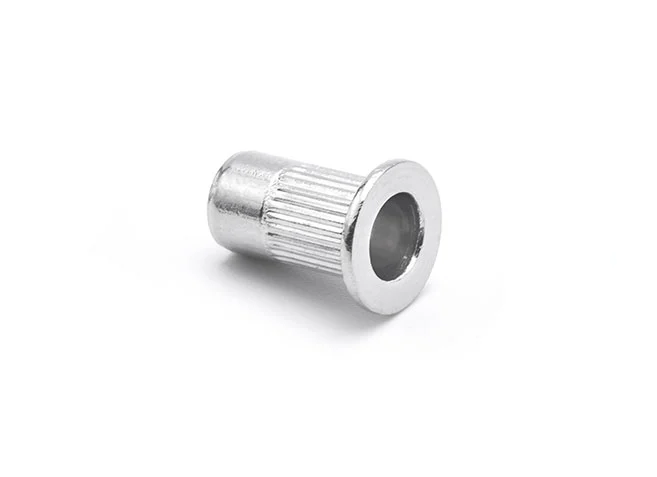 Pull Rivet Nut
Pull Rivet Nut
-
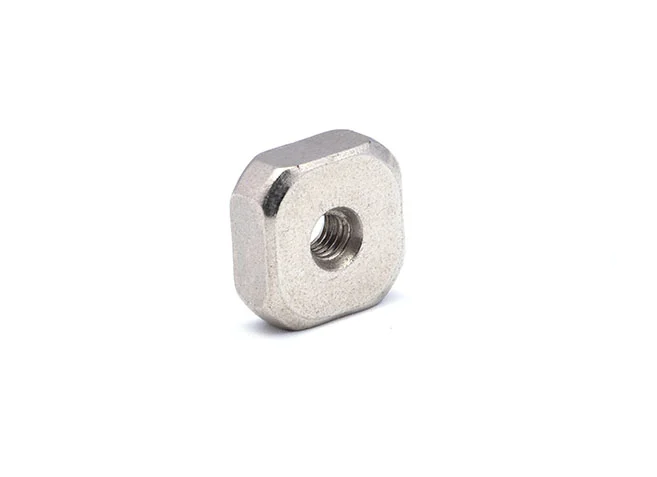 Square Nuts
Square Nuts
-
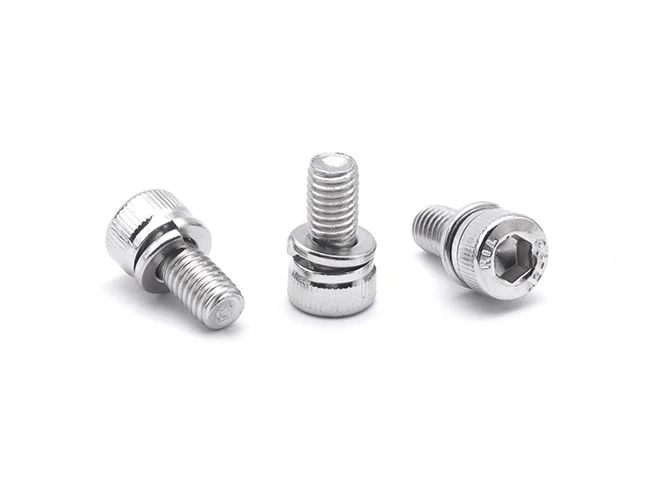 Combination Screws
Combination Screws
-
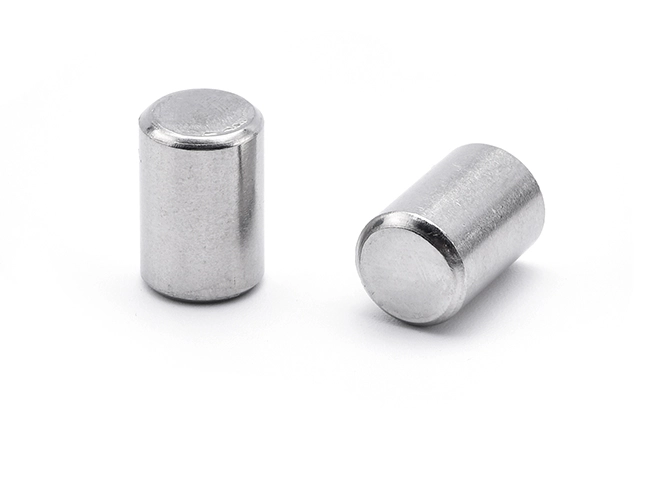 Pin
Pin
-
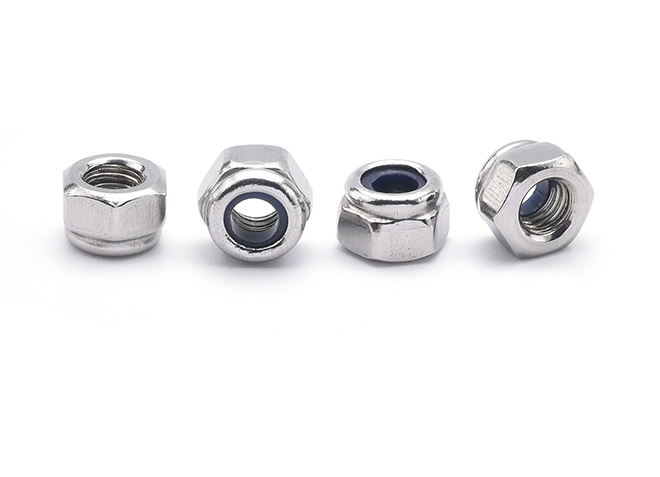 Nylon Locking Nuts
Nylon Locking Nuts
-
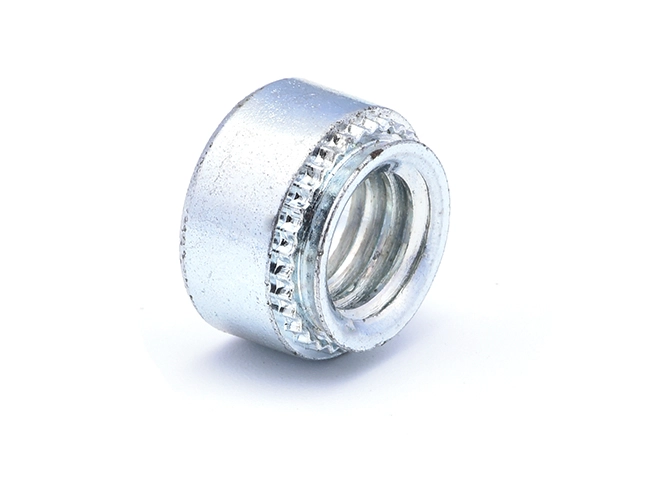 Pressure Rivet Nuts
Pressure Rivet Nuts
-
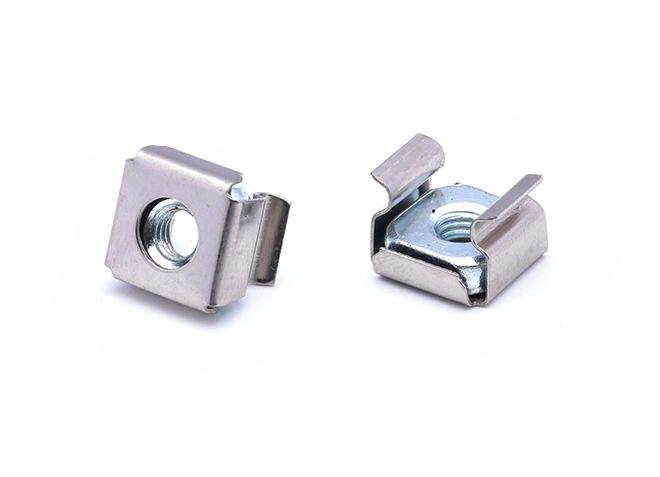 Cage Nut
Cage Nut
-
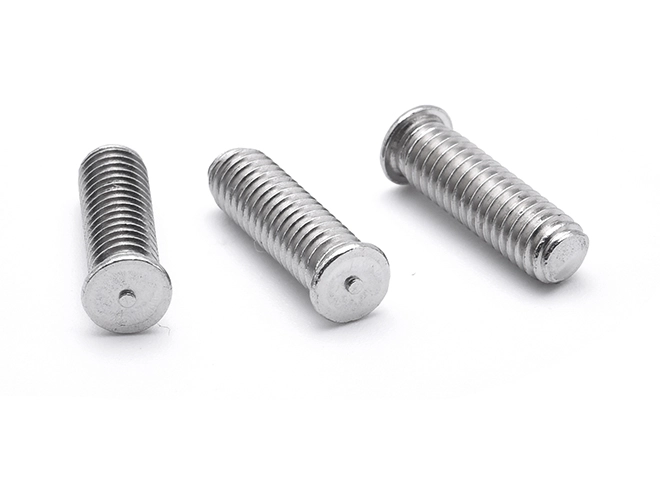 Welding Screws
Welding Screws
-
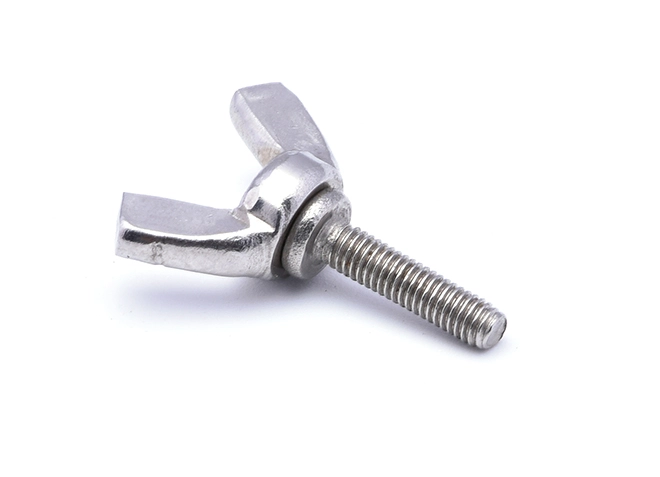 Butterfly Screw
Butterfly Screw
-
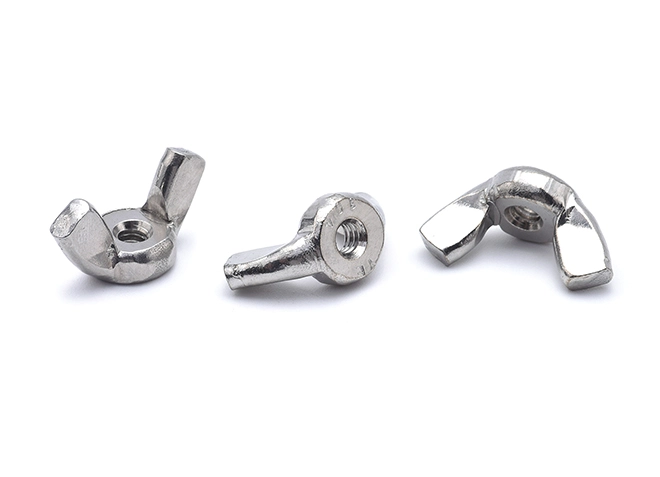 American Standard Butterfly Nut
American Standard Butterfly Nut
-
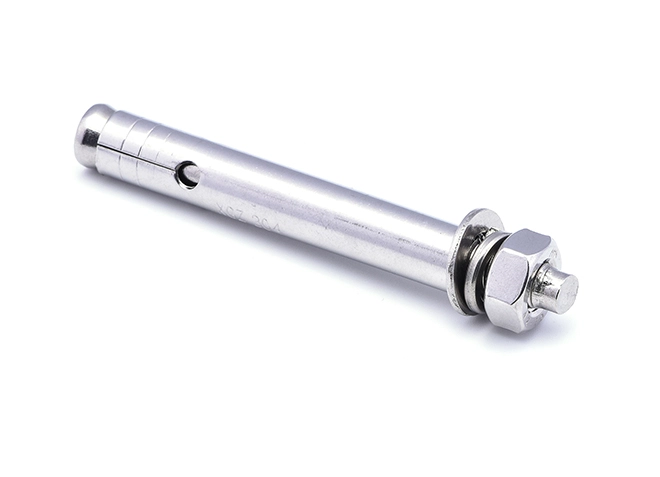 Expansion Screw
Expansion Screw
-
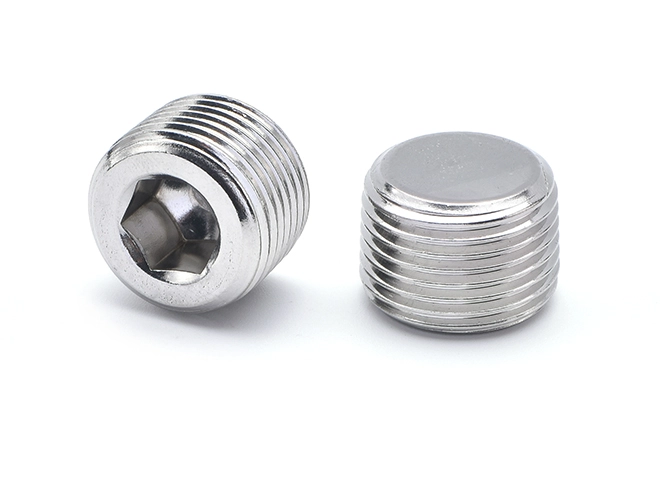 Plug Screw
Plug Screw
-
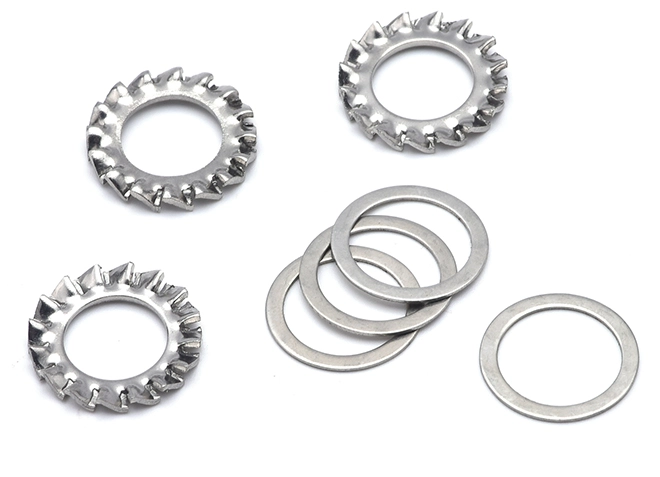 Stainless Steel Washer
Stainless Steel Washer
-
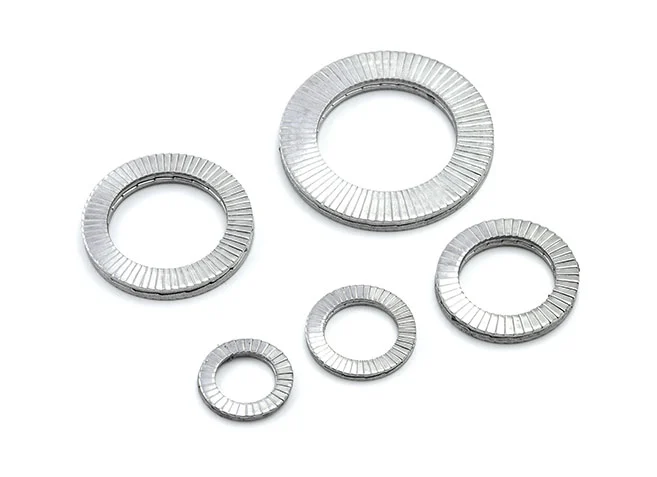 Double Overlap Anti-Loosening Washers
Double Overlap Anti-Loosening Washers
-
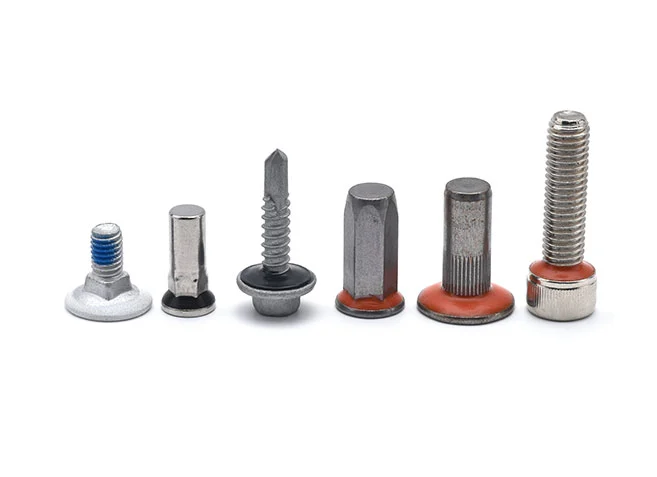 Waterproof and Anti-Drop Screws
Waterproof and Anti-Drop Screws
-
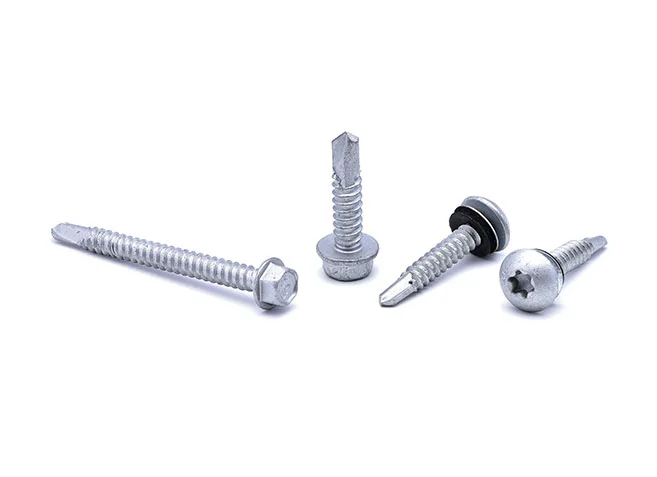 Super Corrosion-Resistant Screws
Super Corrosion-Resistant Screws
-
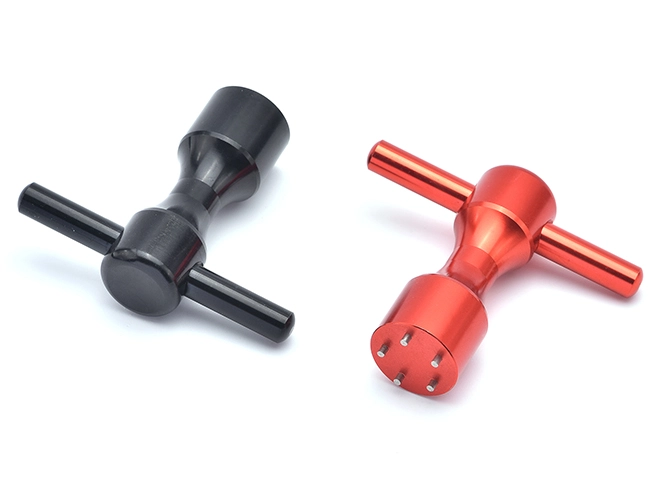 New Type Switchgear
New Type Switchgear
-
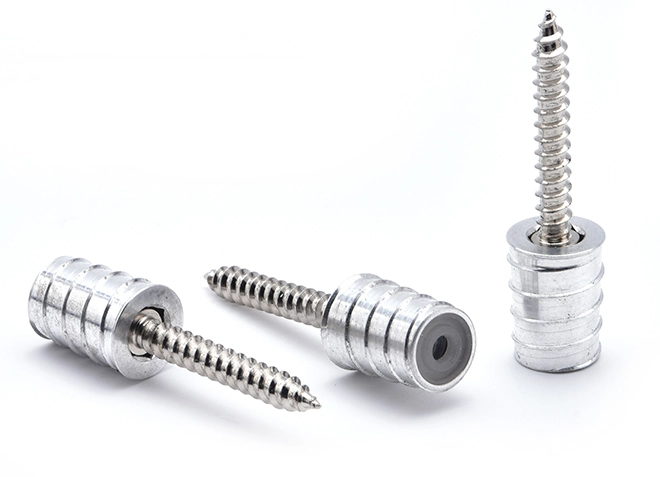 Anti-loose Easy Disassembly Nut Pillar (New Furniture Connector)
Anti-loose Easy Disassembly Nut Pillar (New Furniture Connector)
-
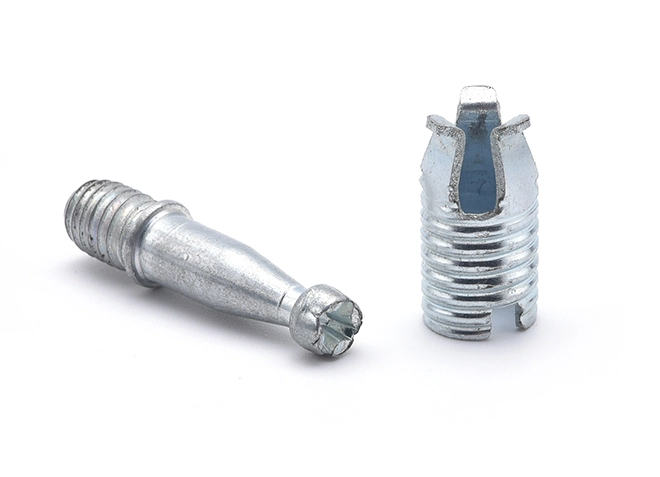 Furniture Simple Assembly and Disassembly Connector
Furniture Simple Assembly and Disassembly Connector
-
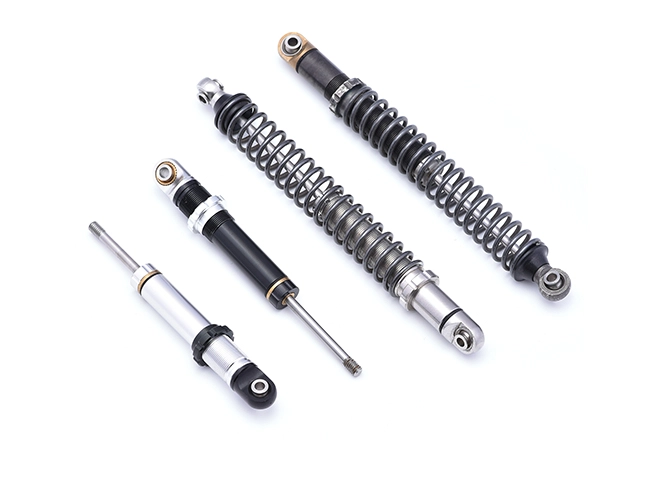 Micro Vibration Absorber
Micro Vibration Absorber
-
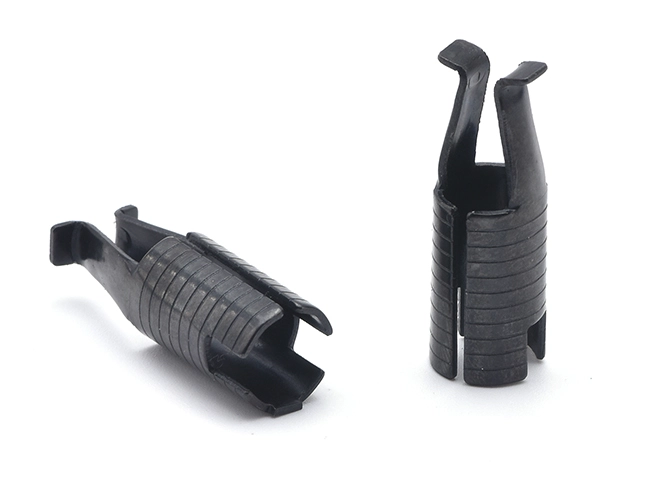 65Mn Material Furniture Connector
65Mn Material Furniture Connector
-
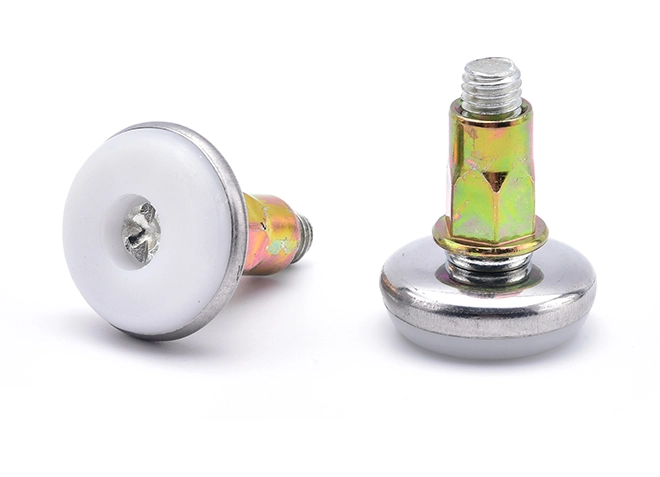 Counter Table Base
Counter Table Base
-
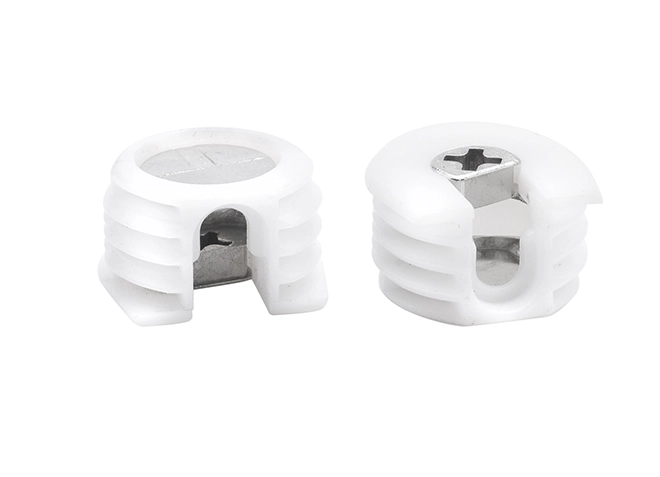 Furniture Connector Nut with Plastic Sleeve
Furniture Connector Nut with Plastic Sleeve
-
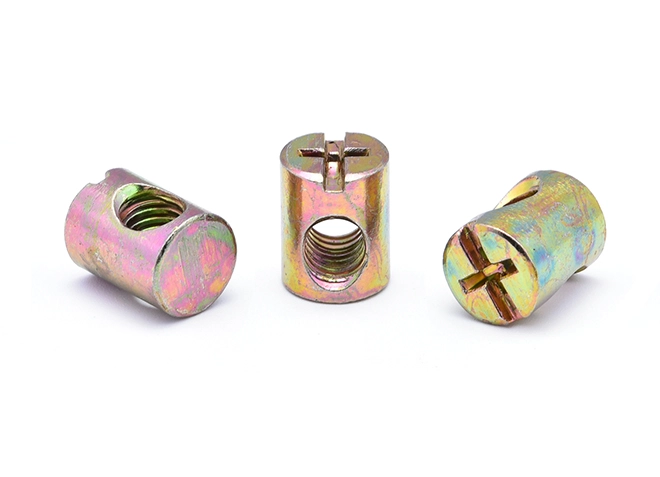 Furniture Horizontal Hole Nut
Furniture Horizontal Hole Nut
-
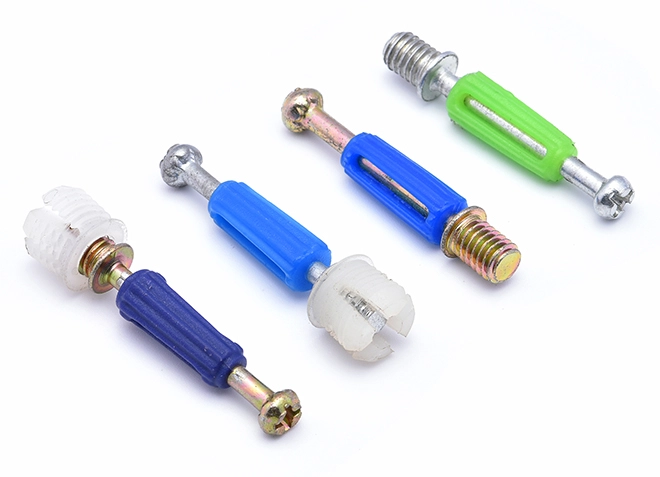 Furniture Connecting Screw
Furniture Connecting Screw
-
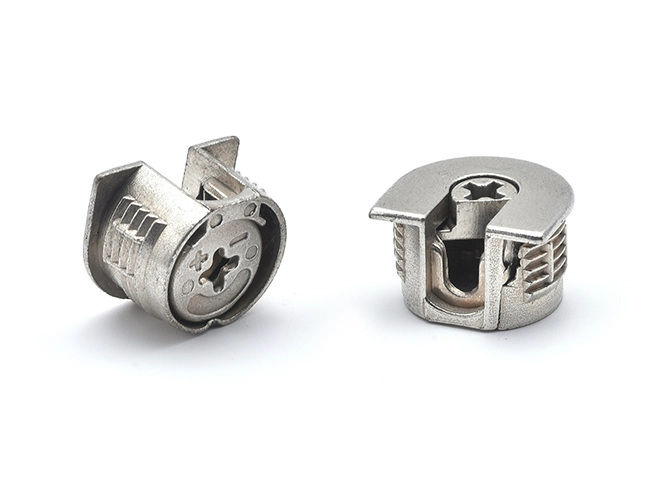 Furniture Connecting Nut Seat
Furniture Connecting Nut Seat
-
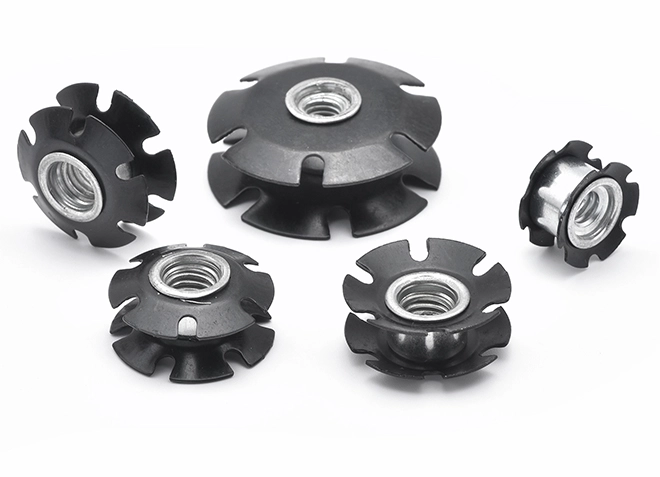 Double Stack Wheels Used On Furniture
Double Stack Wheels Used On Furniture
-
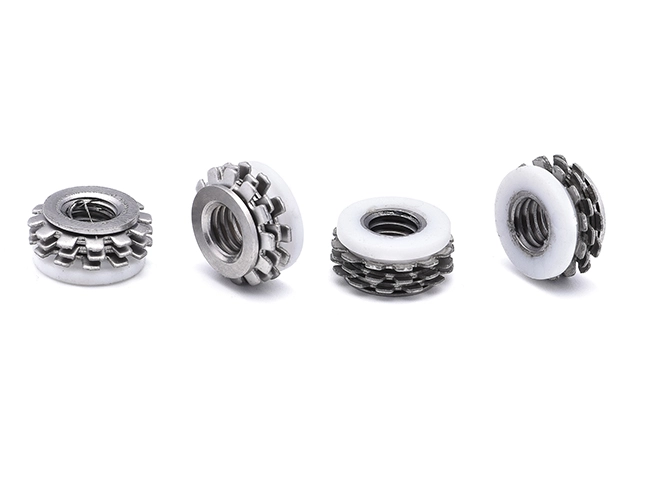 Components Used On Furniture
Components Used On Furniture
-
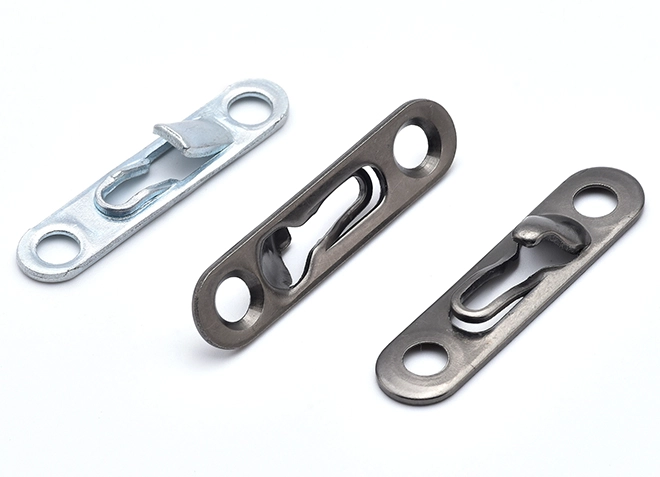 Connection Buckle
Connection Buckle
-
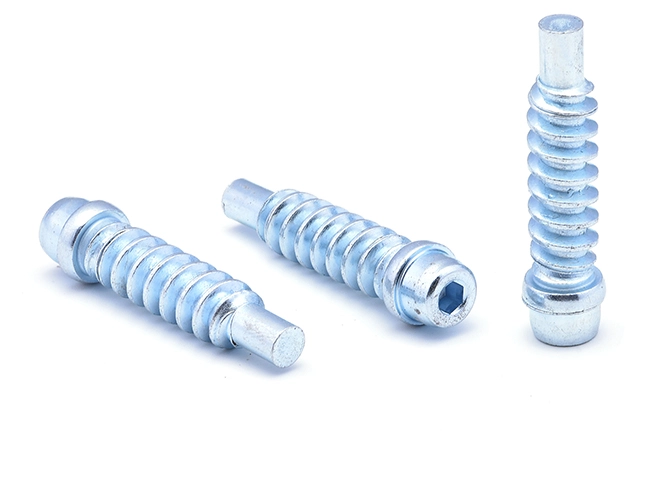 Internal Hexagonal Spiral Screw
Internal Hexagonal Spiral Screw
-
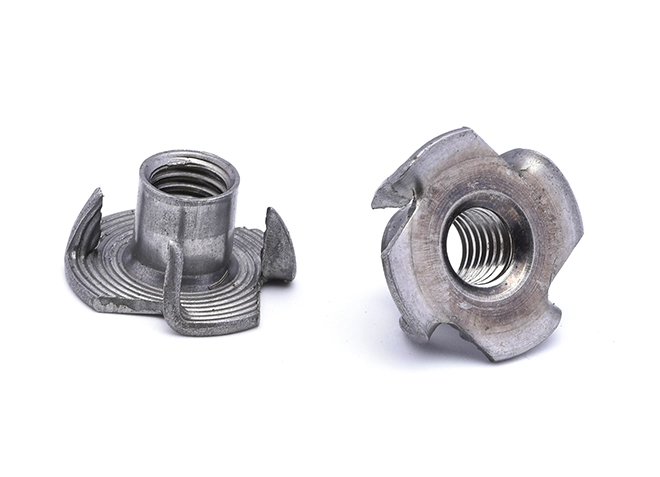 Iron Colored Carbon Steel Four Claw Nut
Iron Colored Carbon Steel Four Claw Nut
-
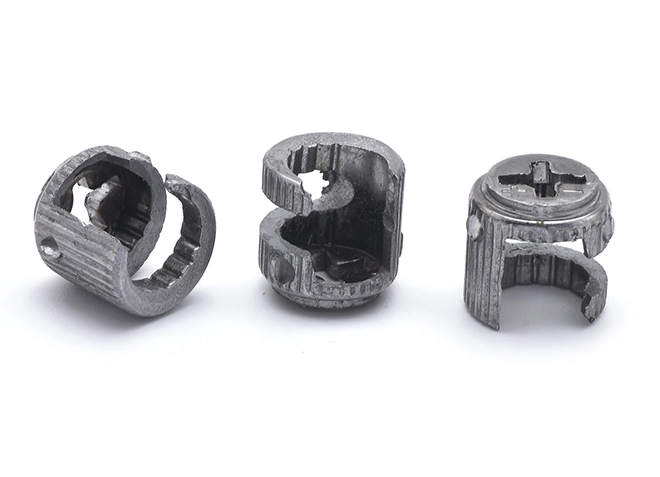 Iron Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
Iron Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
-
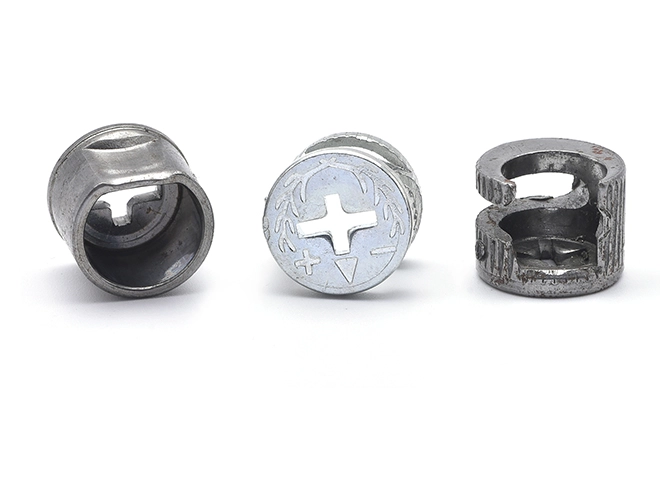 Iron and Zinc Alloy Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
Iron and Zinc Alloy Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
-
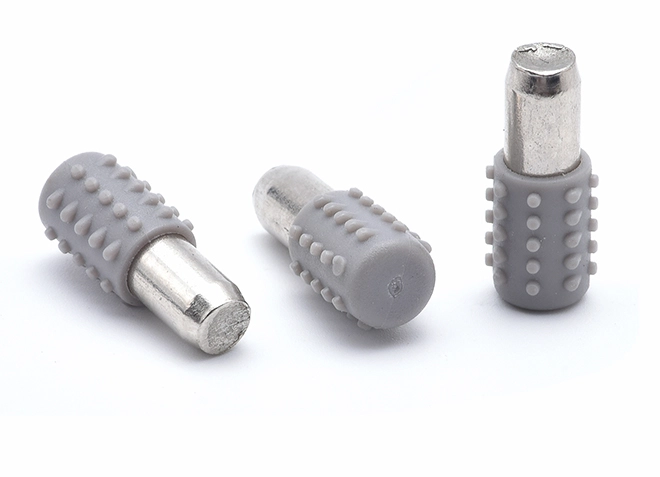 Dowel Pin+ Gray Elephant Rubber Sleeve
Dowel Pin+ Gray Elephant Rubber Sleeve
-
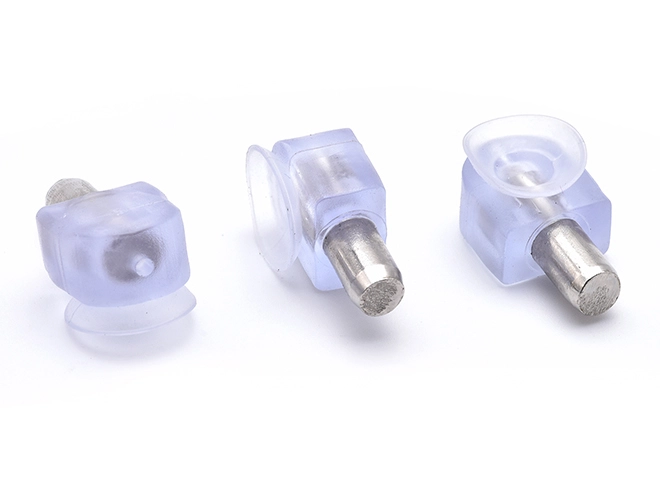 Dowel Pin+ Transparent Elephant Rubber Sleeve
Dowel Pin+ Transparent Elephant Rubber Sleeve
-
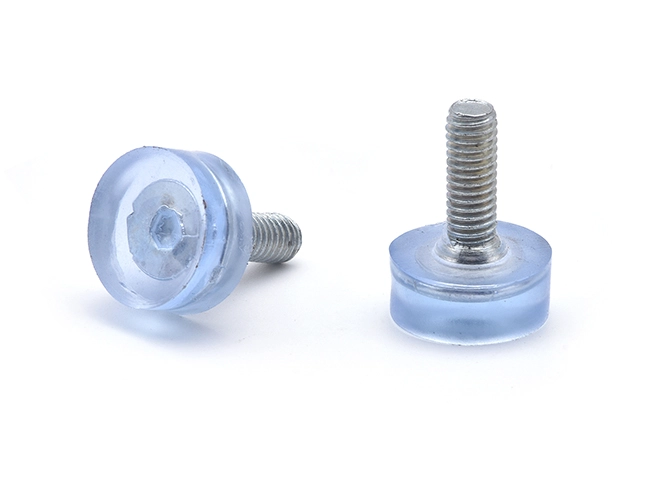 Injection Molded Furniture Foot Pad Screw
Injection Molded Furniture Foot Pad Screw
WHAT ARE YOU LOOKING FOR?