Aaron: +86-18129983931
Max: +86-18922922459
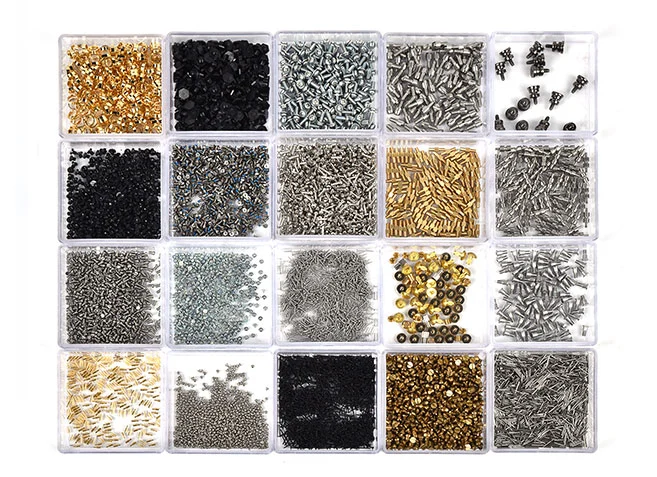
 Micro Screws
Micro Screws
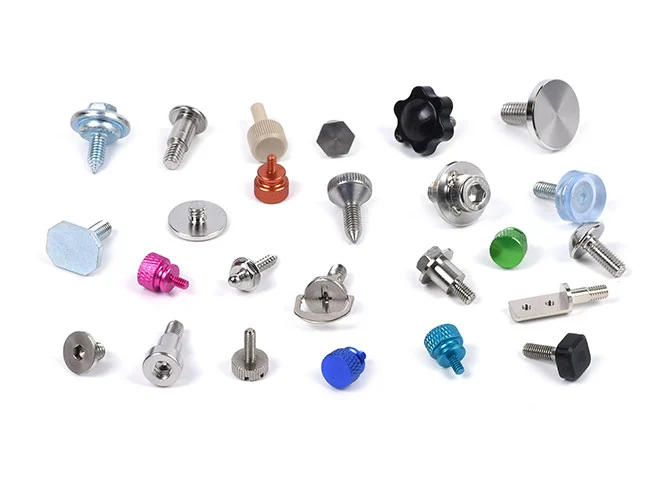 Big Head Screws
Big Head Screws
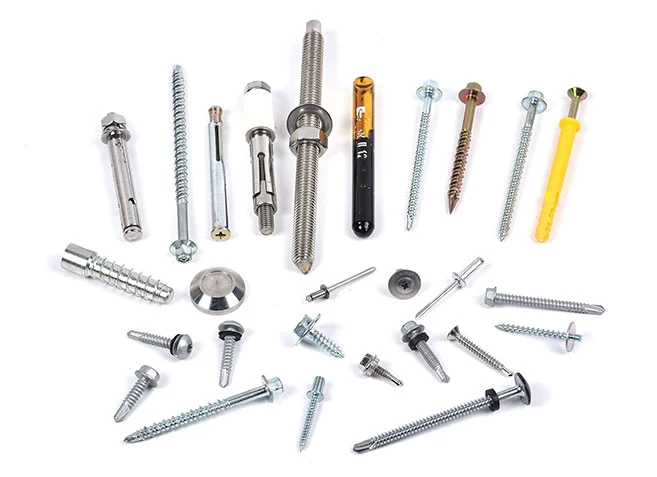 Construction Screws
Construction Screws
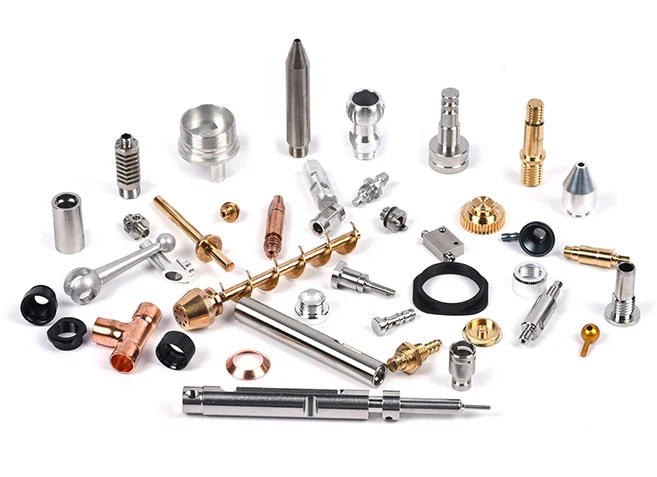 CNC Lathe Machining Parts
CNC Lathe Machining Parts
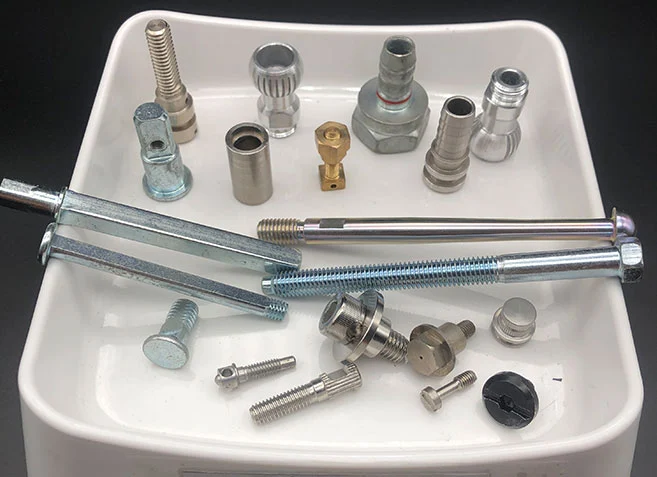 Cold Forged and Undergo Secondary Processing Products
Cold Forged and Undergo Secondary Processing Products
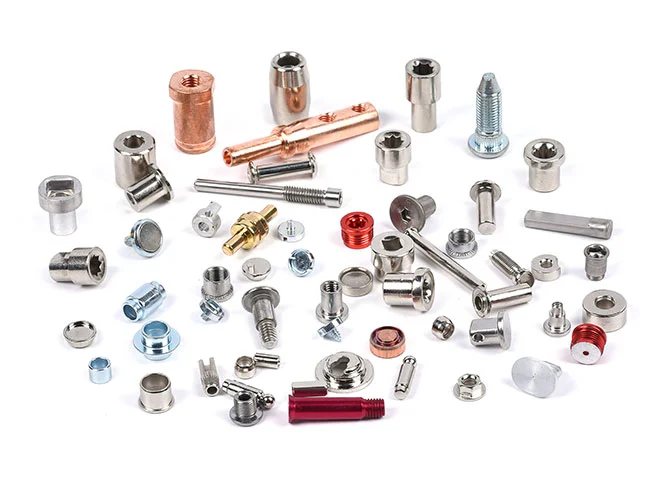 Multi Station Cold Heading Screws
Multi Station Cold Heading Screws
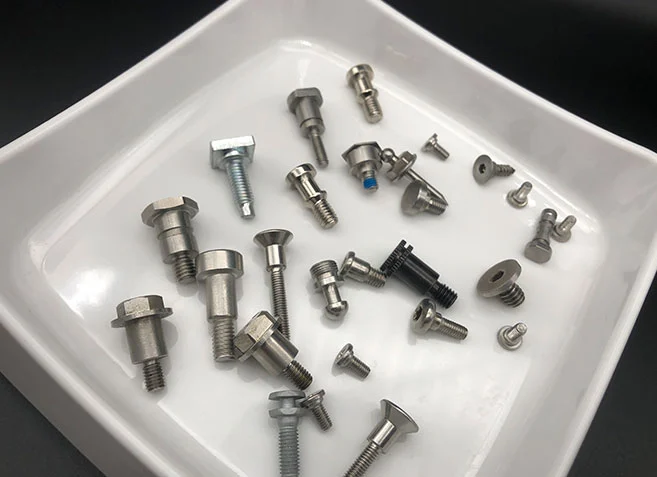 Step Screw
Step Screw
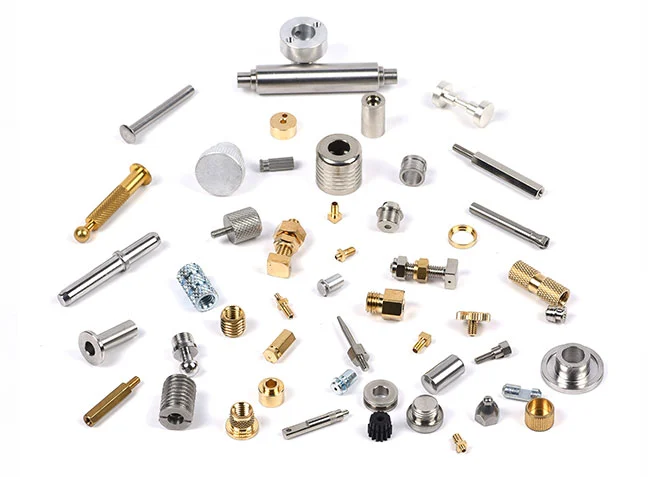 Automatic Lathe Machining Parts
Automatic Lathe Machining Parts
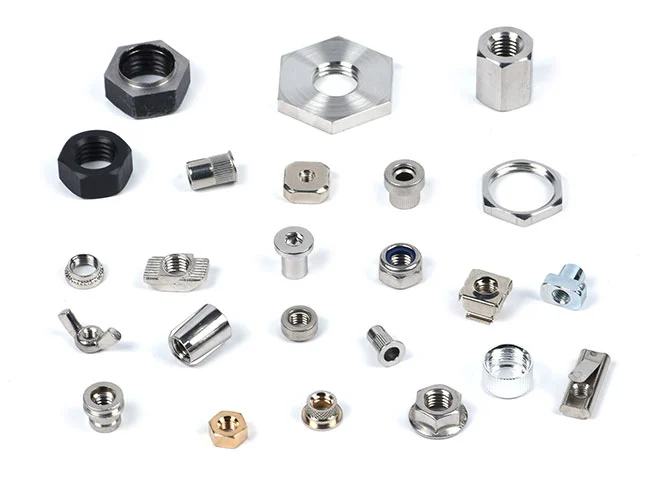 High Difficulty Challenge Cold Heading Fasteners
High Difficulty Challenge Cold Heading Fasteners
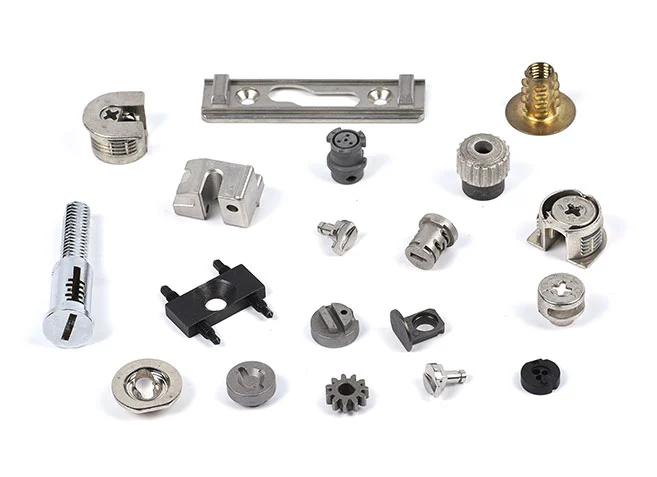 New Tech Fasteners
New Tech Fasteners
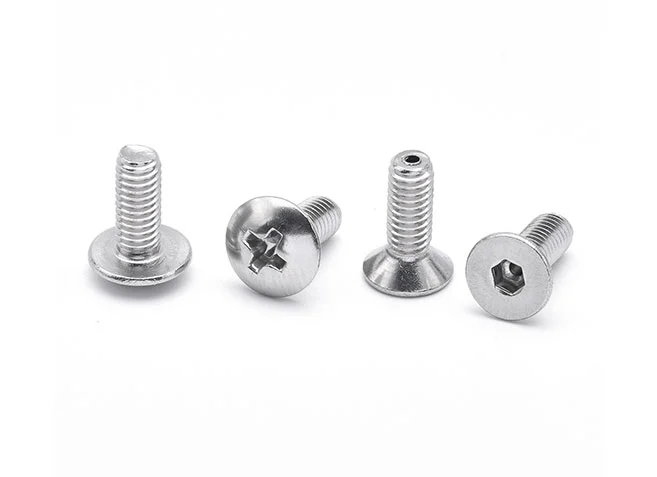 Machine Screws
Machine Screws
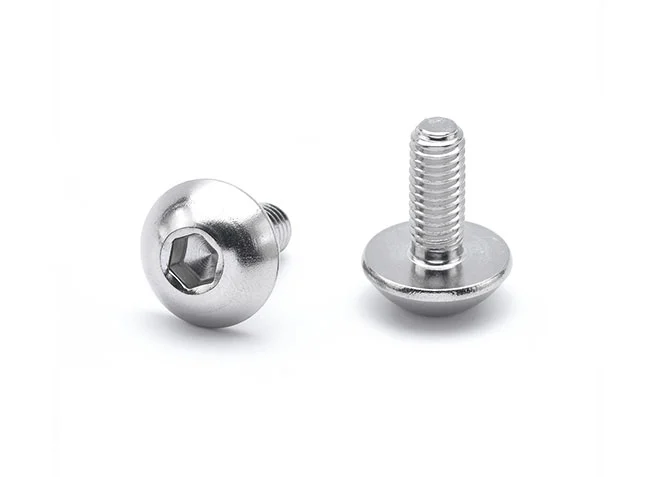 Socket Cap Screws
Socket Cap Screws
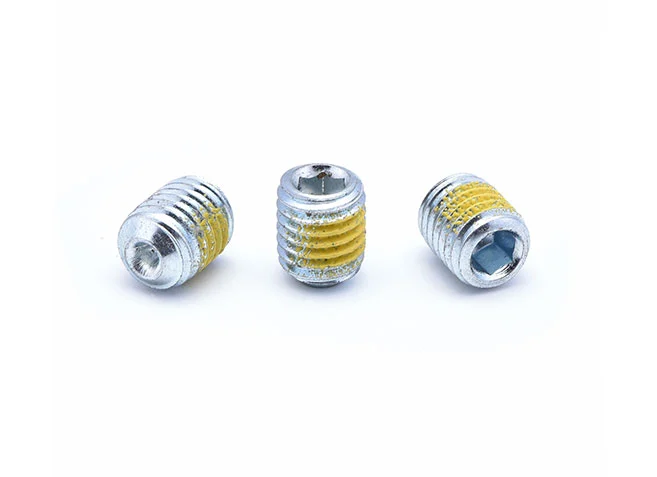 Hexagon Socket Set Screws
Hexagon Socket Set Screws
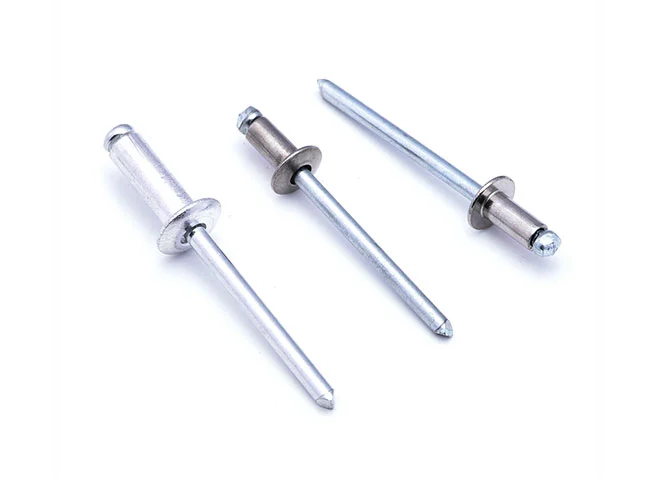 Pull Out Rivet
Pull Out Rivet
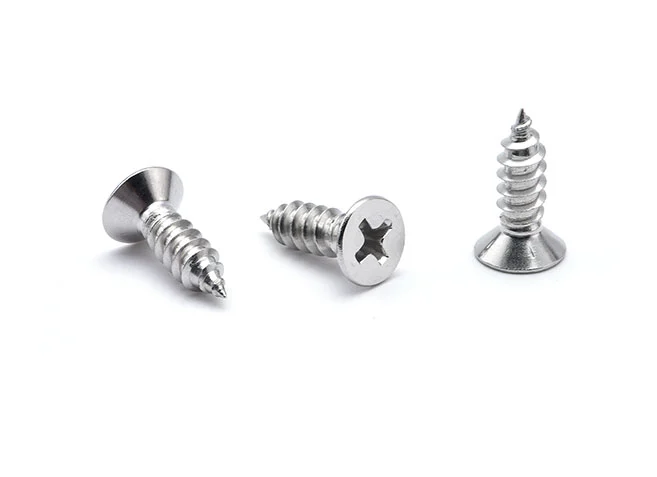 Self Tapping Screws
Self Tapping Screws
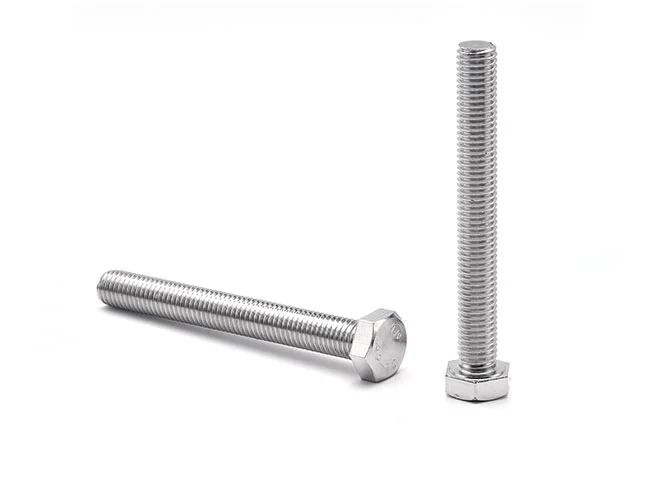 Hex Bolts
Hex Bolts
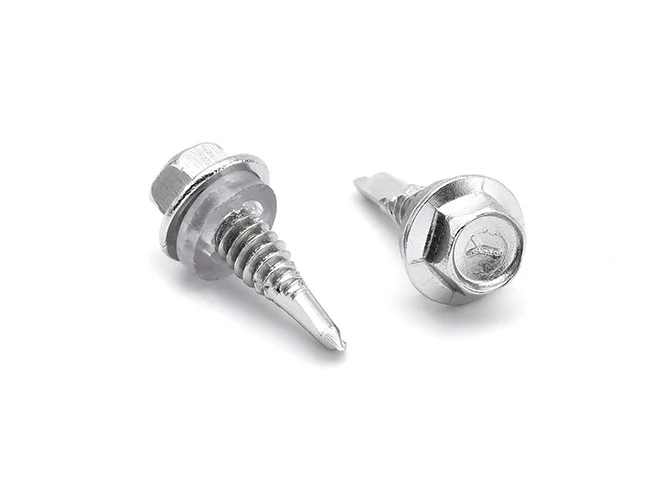 Self Drilling Screws
Self Drilling Screws
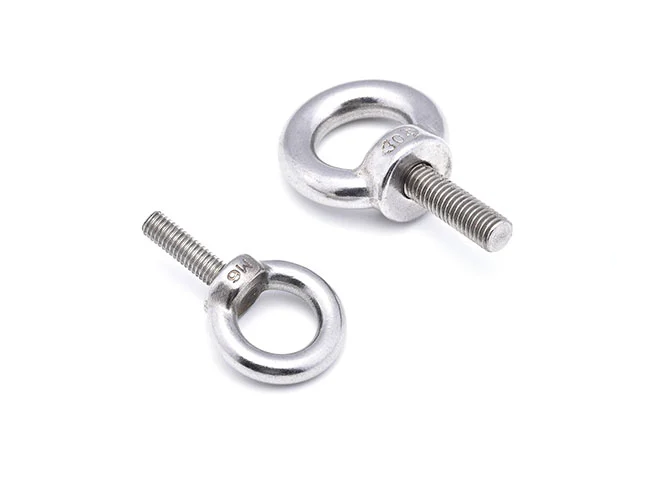 Eye Bolts
Eye Bolts
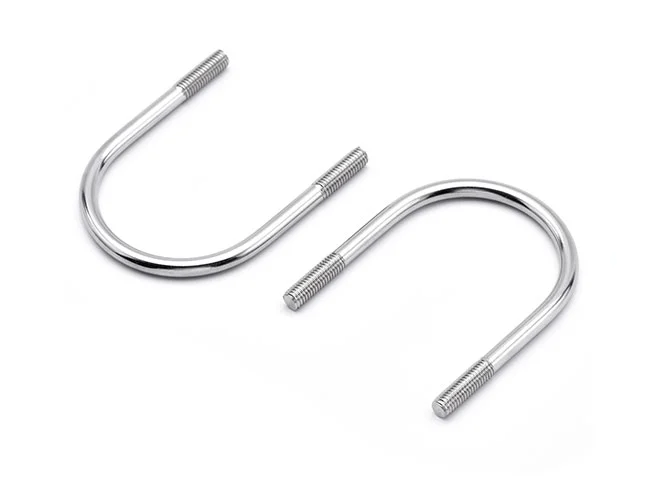 U-bolts
U-bolts
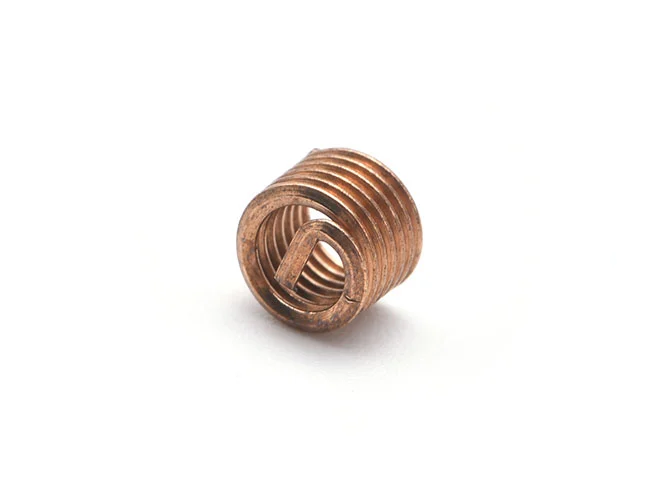 Threaded Sheath
Threaded Sheath
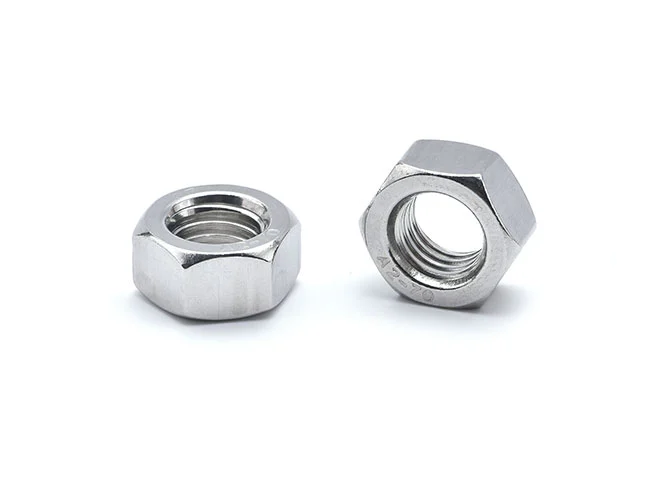 Hex Nut
Hex Nut
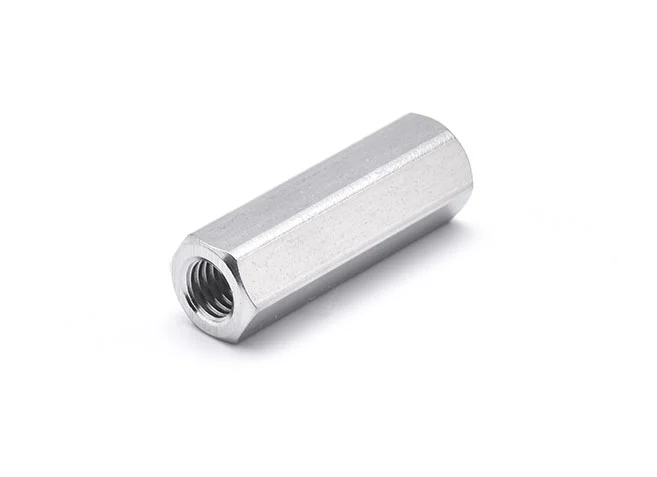 Hex Long Nut
Hex Long Nut
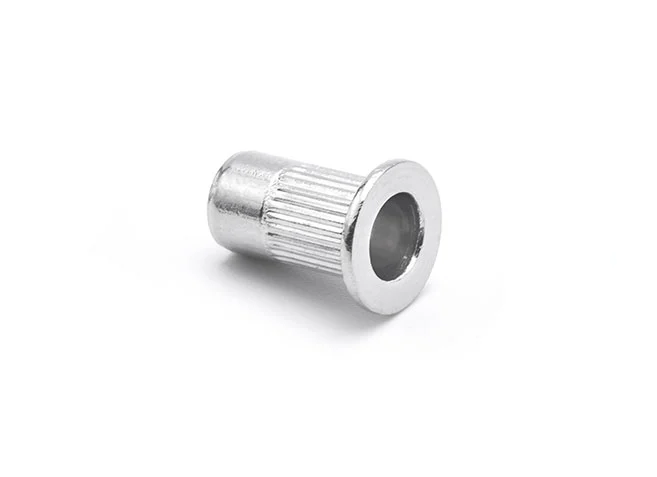 Pull Rivet Nut
Pull Rivet Nut
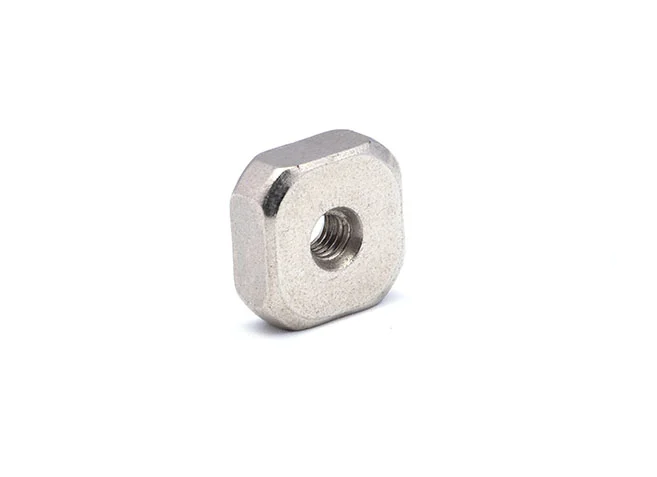 Square Nuts
Square Nuts
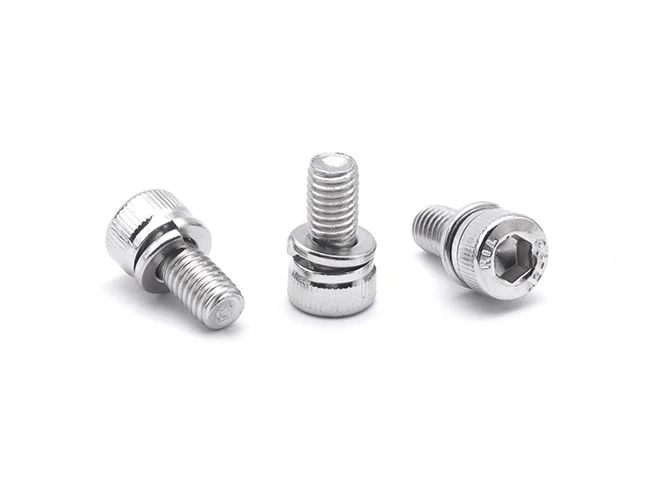 Combination Screws
Combination Screws
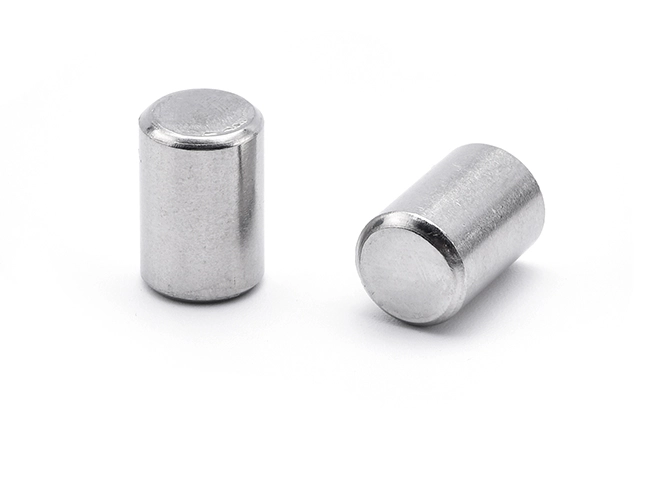 Pin
Pin
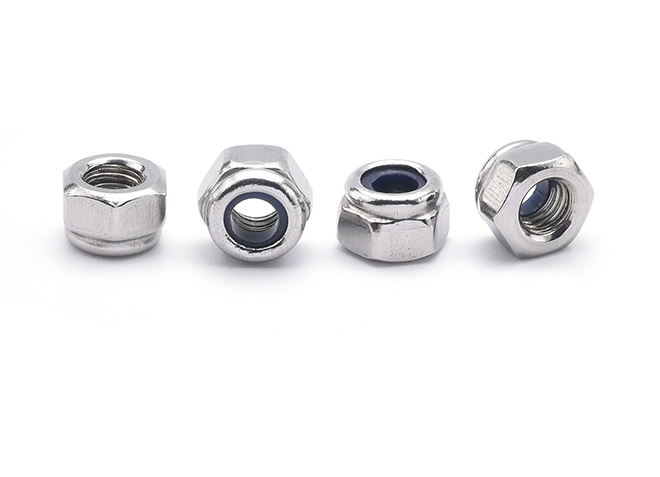 Nylon Locking Nuts
Nylon Locking Nuts
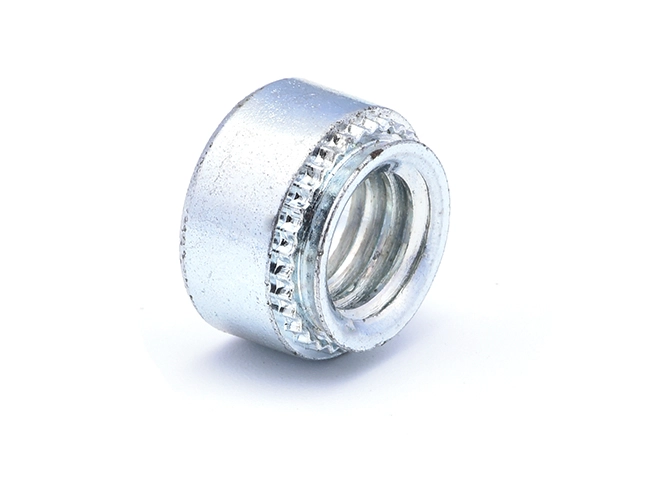 Pressure Rivet Nuts
Pressure Rivet Nuts
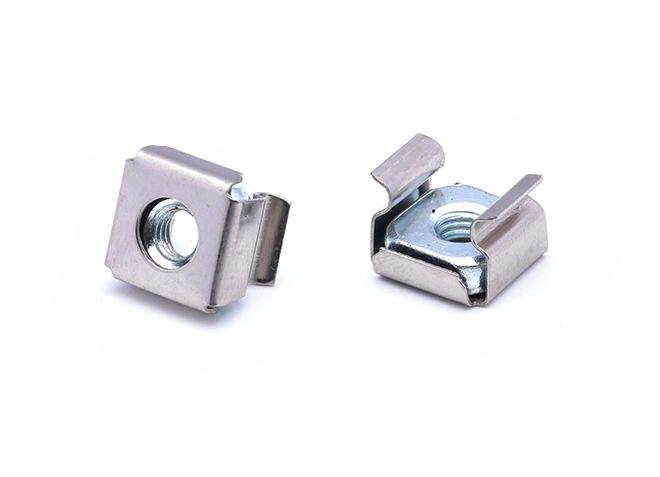 Cage Nut
Cage Nut
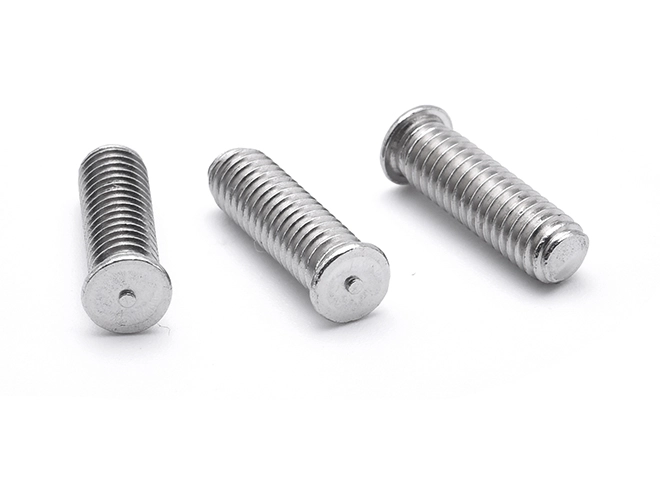 Welding Screws
Welding Screws
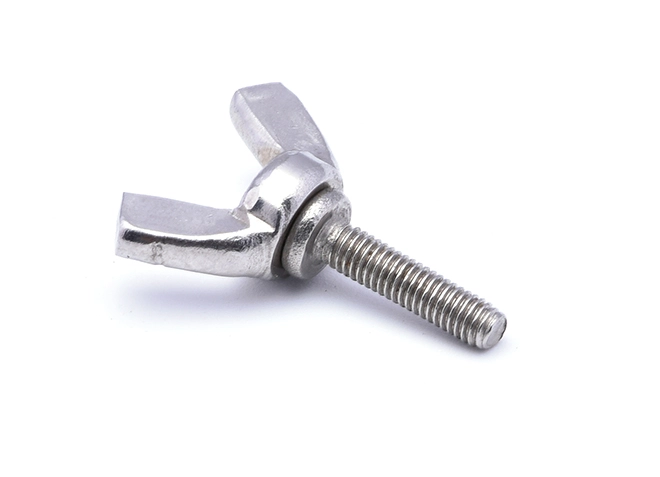 Butterfly Screw
Butterfly Screw
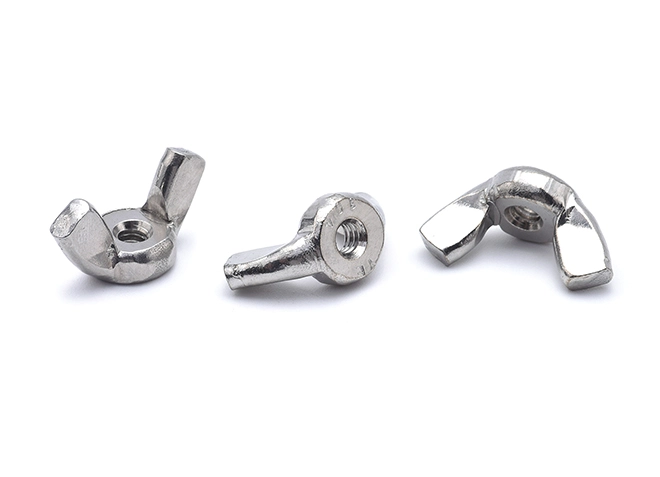 American Standard Butterfly Nut
American Standard Butterfly Nut
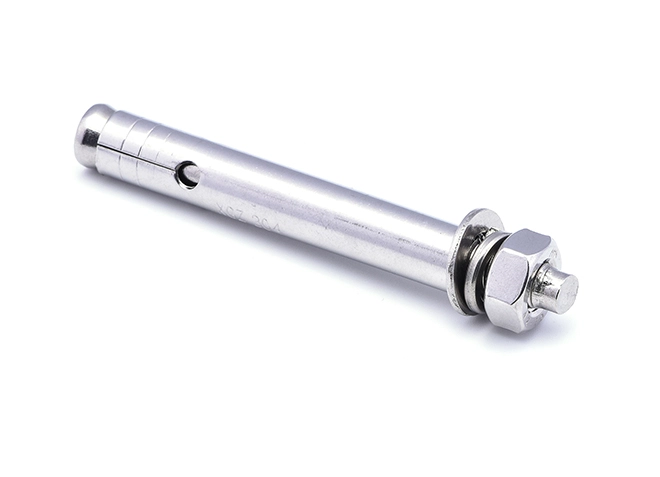 Expansion Screw
Expansion Screw
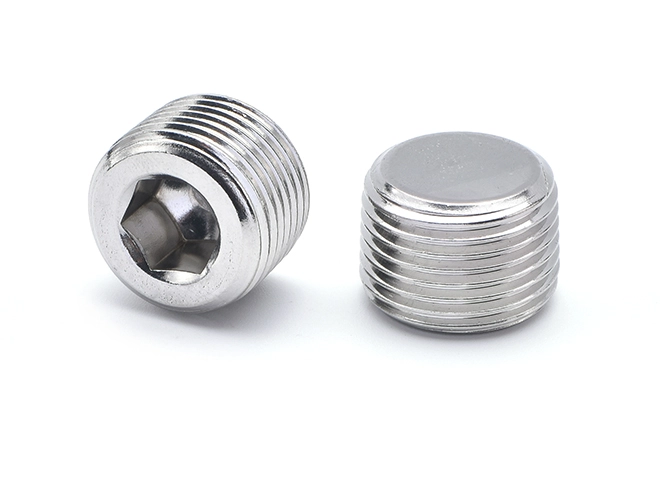 Plug Screw
Plug Screw
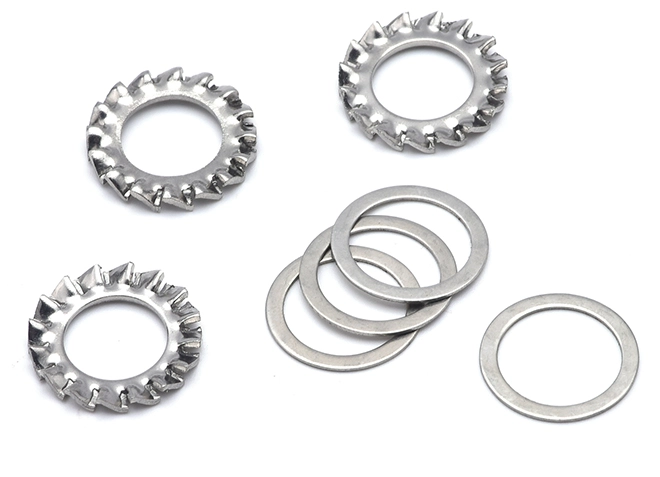 Stainless Steel Washer
Stainless Steel Washer
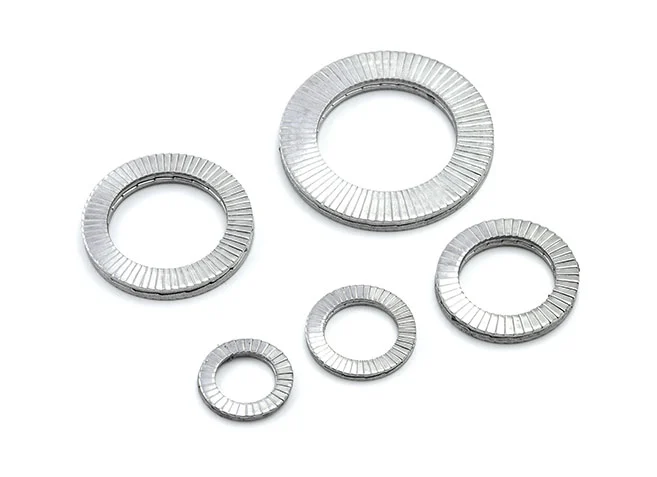 Double Overlap Anti-Loosening Washers
Double Overlap Anti-Loosening Washers
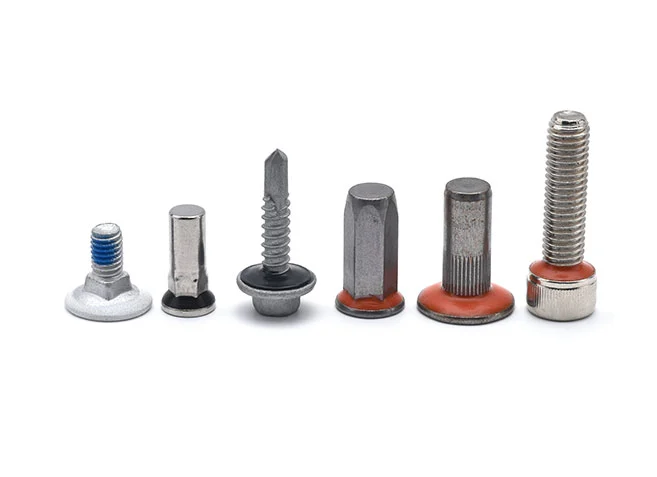 Waterproof and Anti-Drop Screws
Waterproof and Anti-Drop Screws
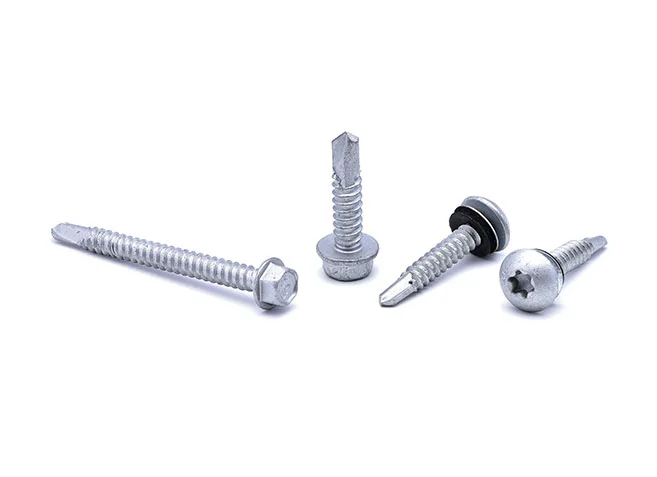 Super Corrosion-Resistant Screws
Super Corrosion-Resistant Screws
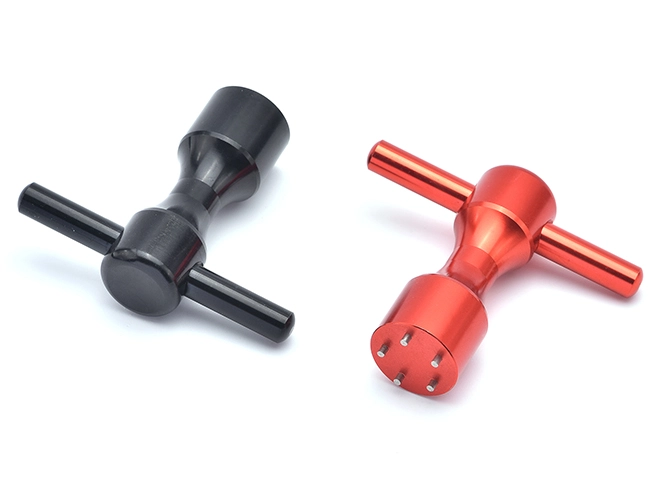 New Type Switchgear
New Type Switchgear
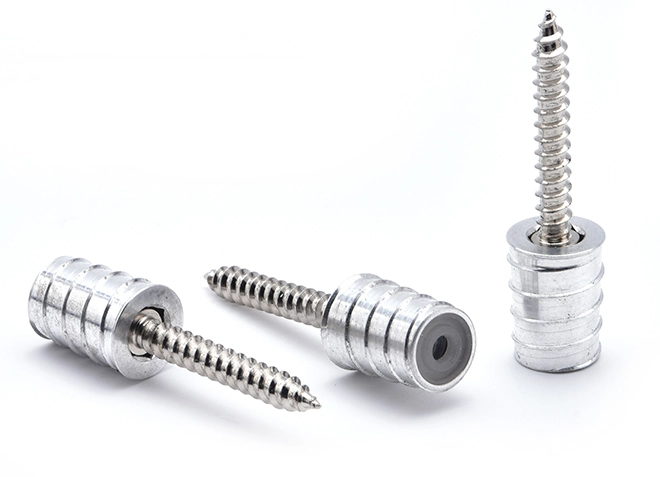 Anti-loose Easy Disassembly Nut Pillar (New Furniture Connector)
Anti-loose Easy Disassembly Nut Pillar (New Furniture Connector)
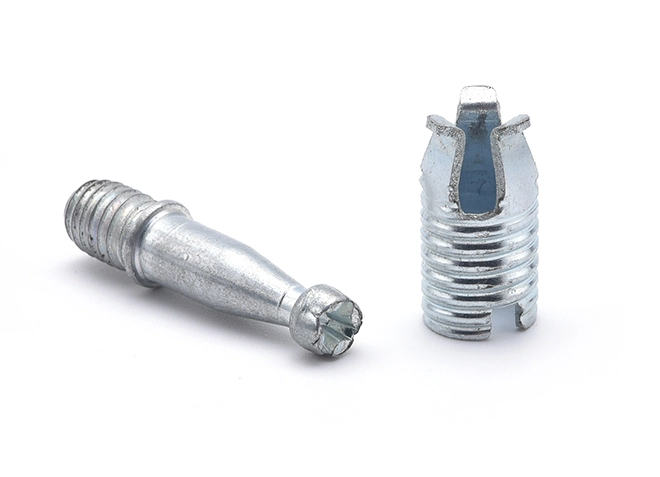 Furniture Simple Assembly and Disassembly Connector
Furniture Simple Assembly and Disassembly Connector
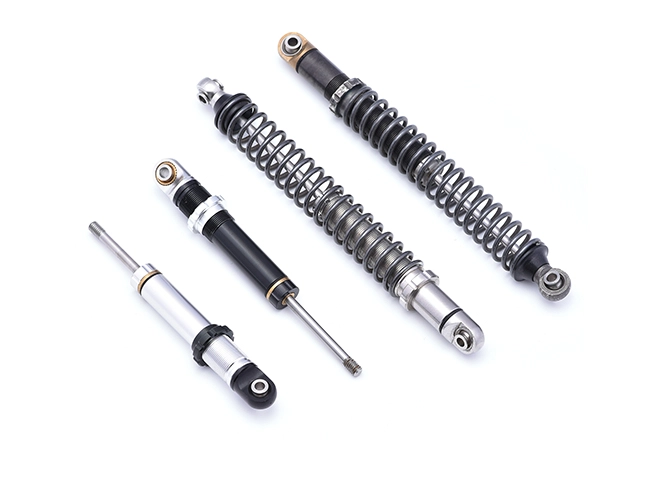 Micro Vibration Absorber
Micro Vibration Absorber
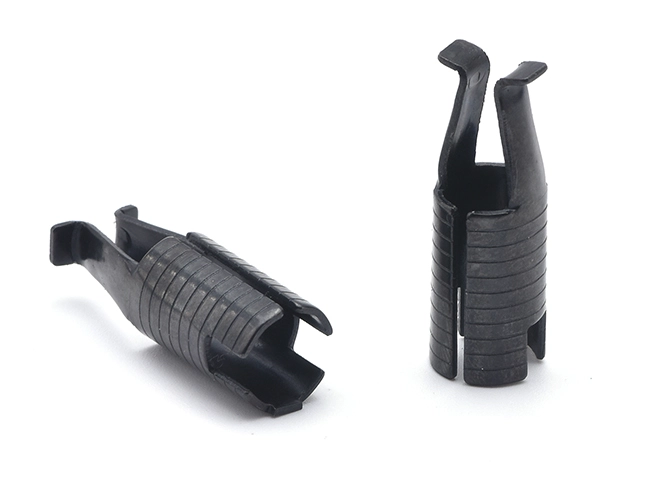 65Mn Material Furniture Connector
65Mn Material Furniture Connector
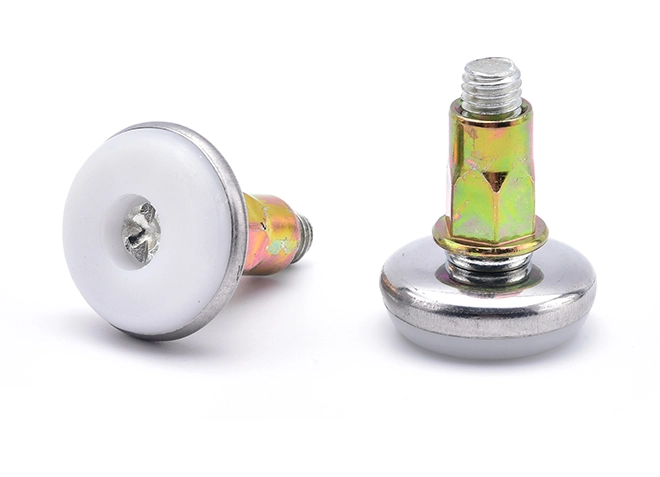 Counter Table Base
Counter Table Base
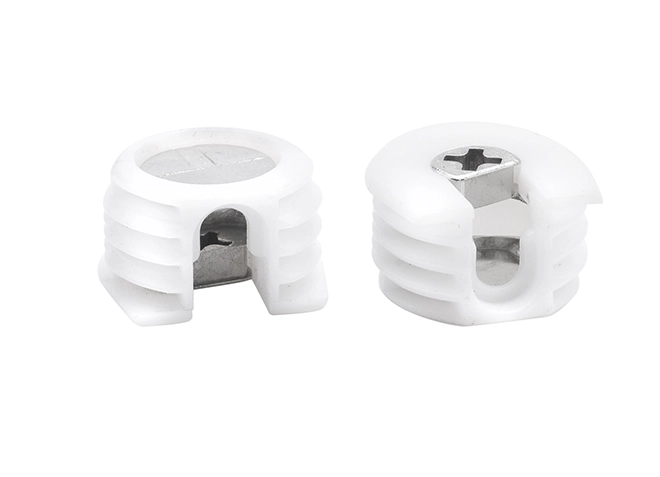 Furniture Connector Nut with Plastic Sleeve
Furniture Connector Nut with Plastic Sleeve
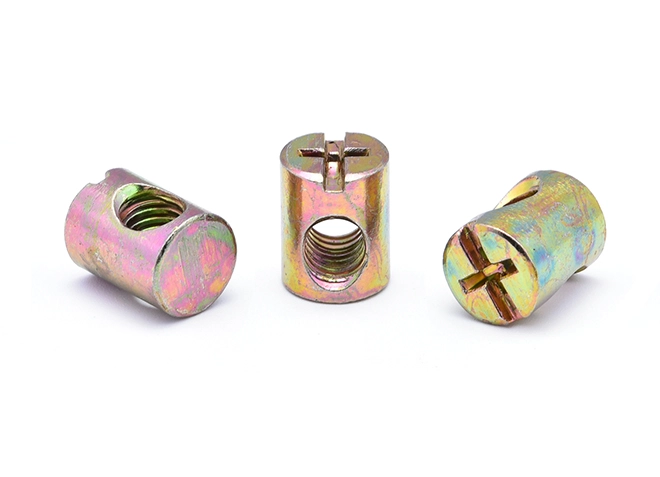 Furniture Horizontal Hole Nut
Furniture Horizontal Hole Nut
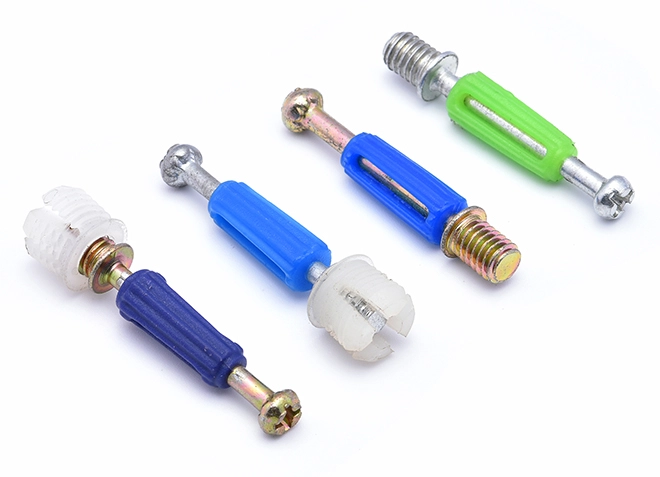 Furniture Connecting Screw
Furniture Connecting Screw
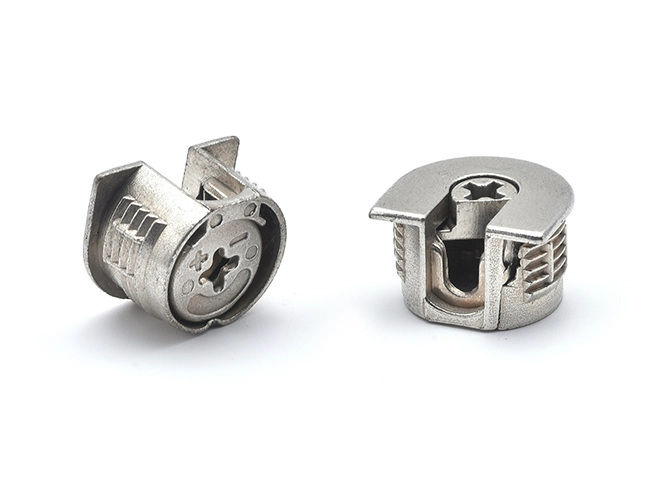 Furniture Connecting Nut Seat
Furniture Connecting Nut Seat
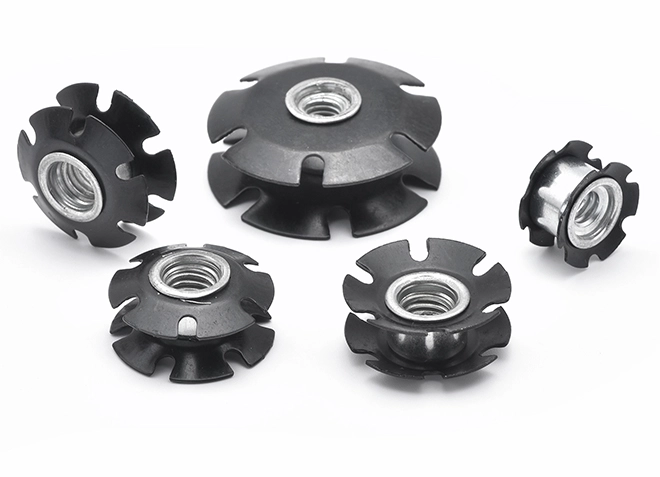 Double Stack Wheels Used On Furniture
Double Stack Wheels Used On Furniture
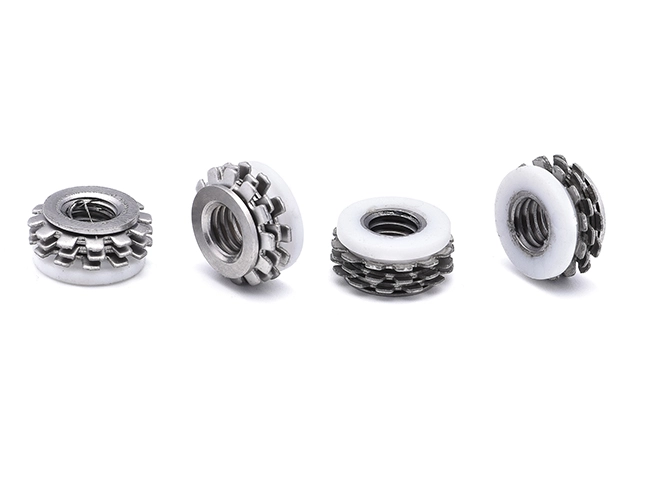 Components Used On Furniture
Components Used On Furniture
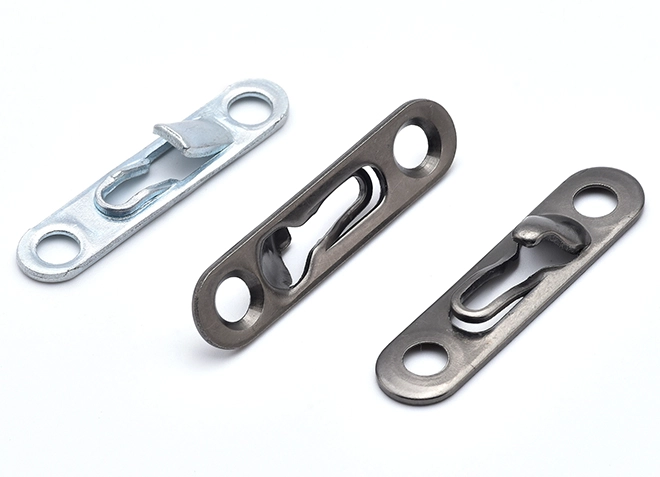 Connection Buckle
Connection Buckle
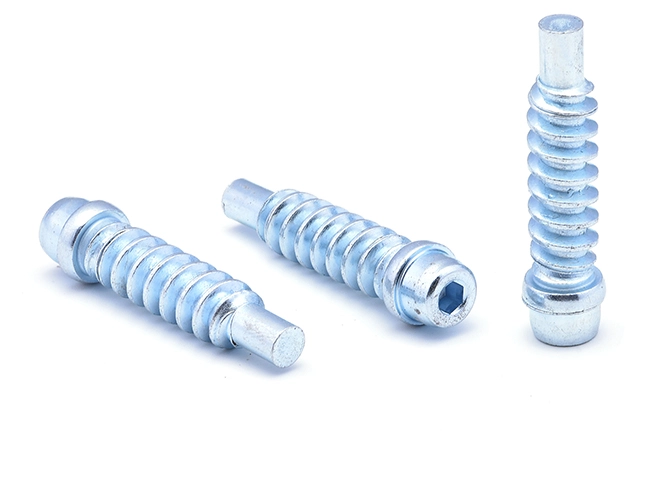 Internal Hexagonal Spiral Screw
Internal Hexagonal Spiral Screw
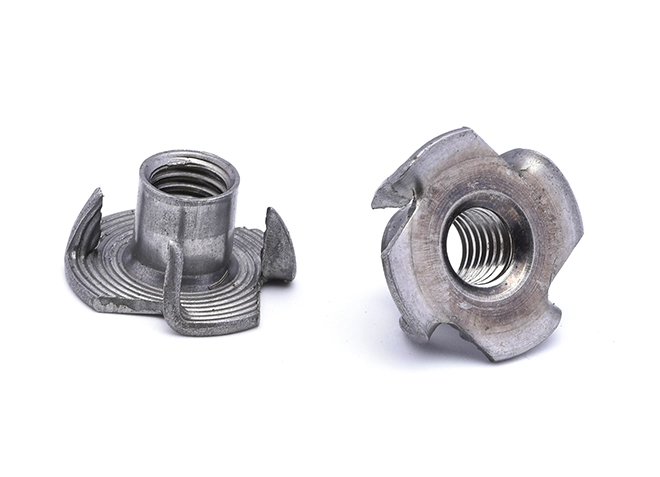 Iron Colored Carbon Steel Four Claw Nut
Iron Colored Carbon Steel Four Claw Nut
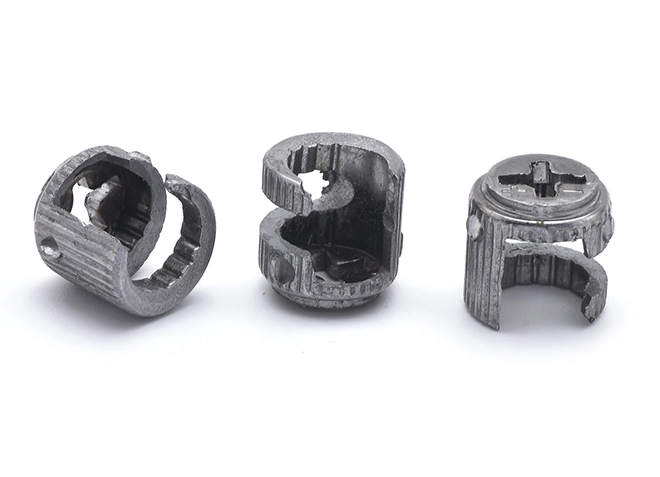 Iron Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
Iron Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
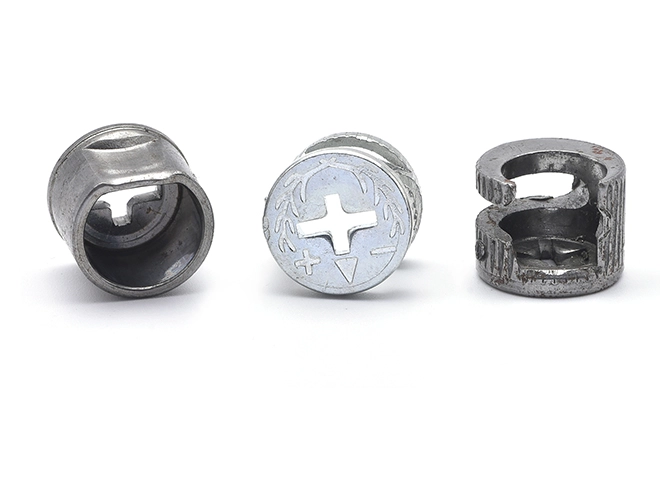 Iron and Zinc Alloy Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
Iron and Zinc Alloy Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
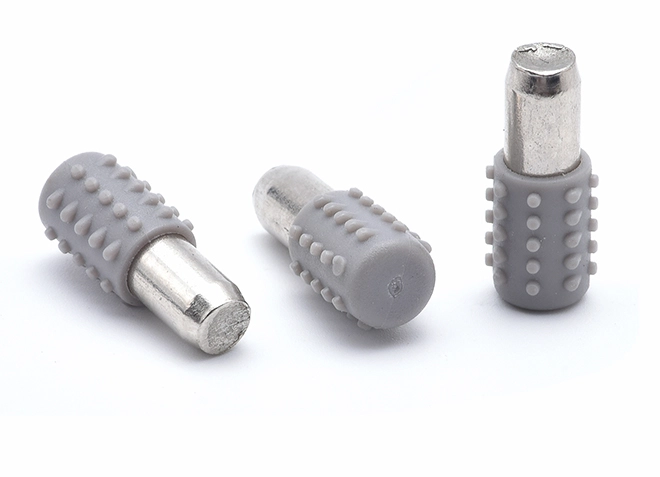 Dowel Pin+ Gray Elephant Rubber Sleeve
Dowel Pin+ Gray Elephant Rubber Sleeve
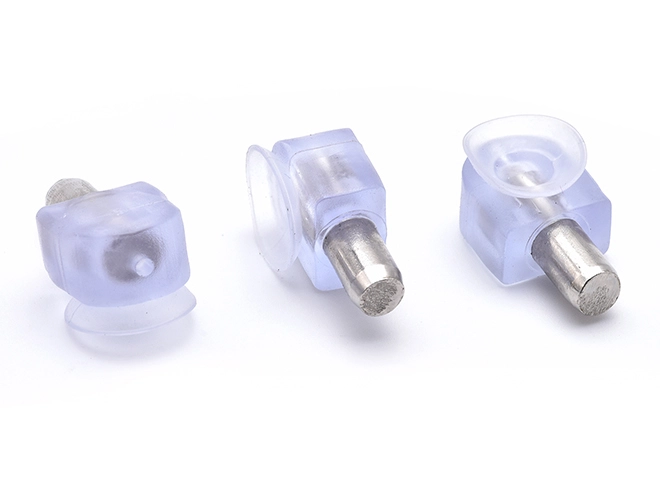 Dowel Pin+ Transparent Elephant Rubber Sleeve
Dowel Pin+ Transparent Elephant Rubber Sleeve
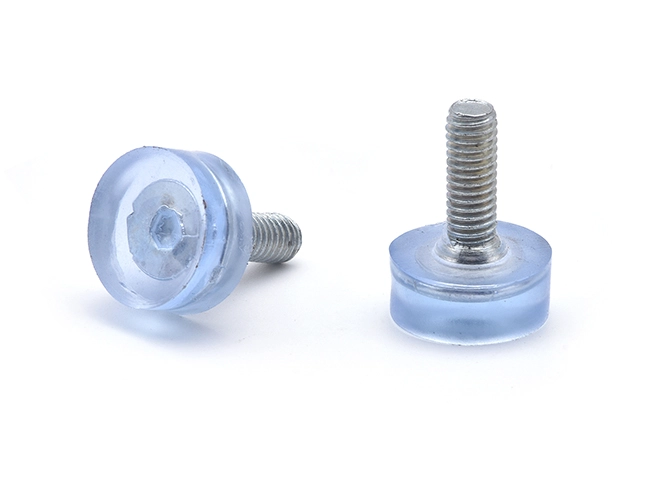 Injection Molded Furniture Foot Pad Screw
Injection Molded Furniture Foot Pad Screw

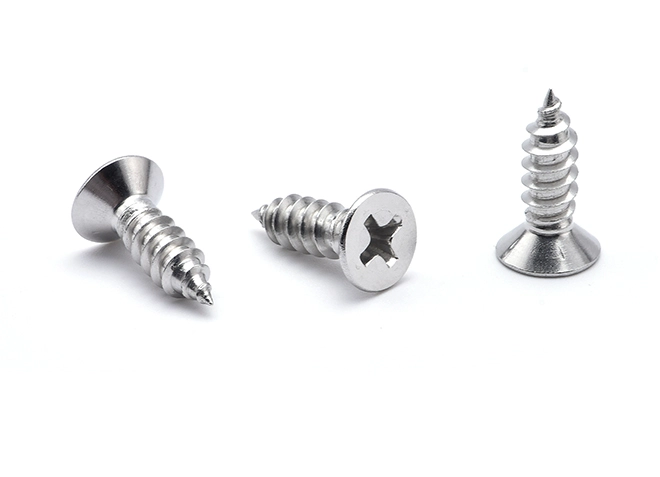
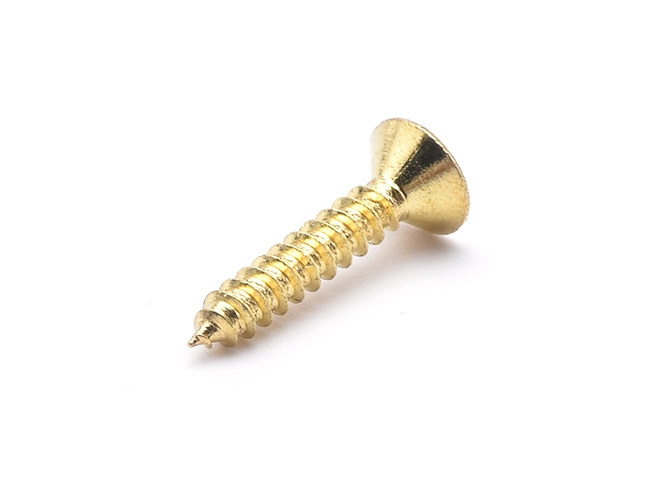
Self-tapping screws are a type of fastener that is designed to tap its own thread into the material in which it is driven, eliminating the need for a pre-tapped hole. This ability makes them highly convenient for a variety of construction and manufacturing applications, particularly in materials like wood, plastic, and metal. Self-tapping screws are widely used because they simplify the assembly process and reduce the time and cost associated with thread cutting.
Material: Select a screw made from a material compatible with the material you're fastening. Common options include steel, stainless steel, and brass. For outdoor or corrosive environments, stainless steel or coated screws are preferable.
Screw Type:
Thread Type: Choose between coarse or fine threads based on the material. Coarse threads are generally better for softer materials like wood, while fine threads are suitable for metal or hard materials.
Point Style: Self-tapping screws come with various point styles:
Sharp Point: For wood or softer materials.
Type A or B Point: For metal or plastic.
Size and Length: Ensure the screw length is appropriate for the thickness of the material you’re fastening. The diameter should be compatible with the size of the pre-drilled hole or the thickness of the material.
Head Type: Choose the head type that suits your needs, such as flat, pan, or oval. The head type affects the appearance and how the screw will be driven and secured.
Thread Design: Full Thread: For a strong grip over the entire length of the screw.
Partial Thread: For applications where only a portion of the screw needs to engage with the material.
Drive Type: Consider the drive type, such as Phillips, slotted, or Torx. Select one that matches your tools and provides the desired level of torque and ease of installation.
By evaluating these factors, you can choose a self-tapping screw that ensures a secure and reliable fastening for your specific application.
arron18129983931@gmail.com
arron18129983931@gmail.com
arron18129983931@gmail.com








