Aaron: +86-18129983931
Max: +86-18922922459
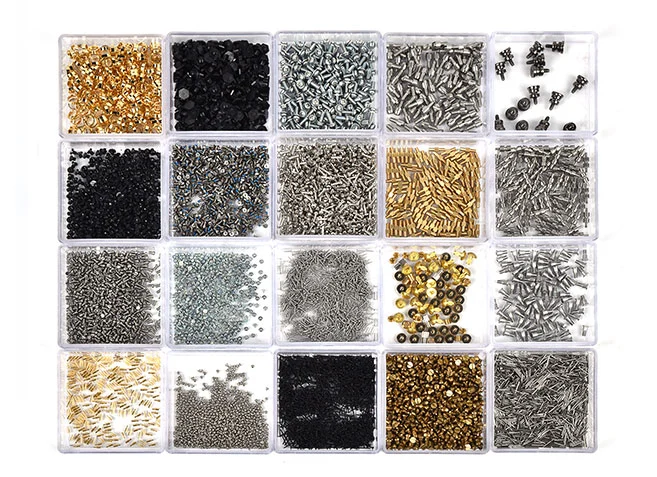
 Micro Screws
Micro Screws
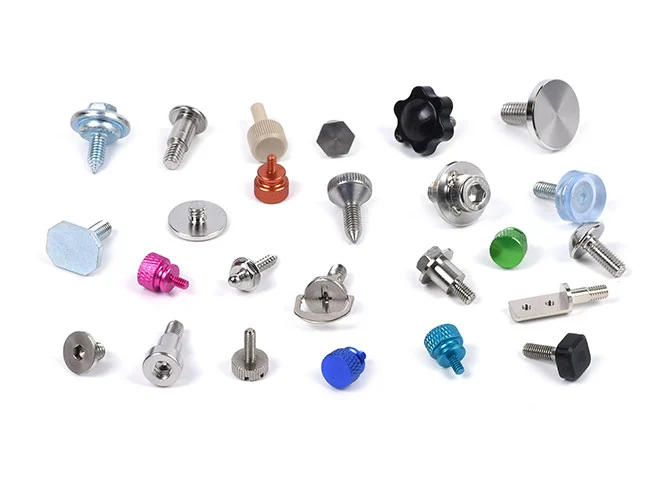 Big Head Screws
Big Head Screws
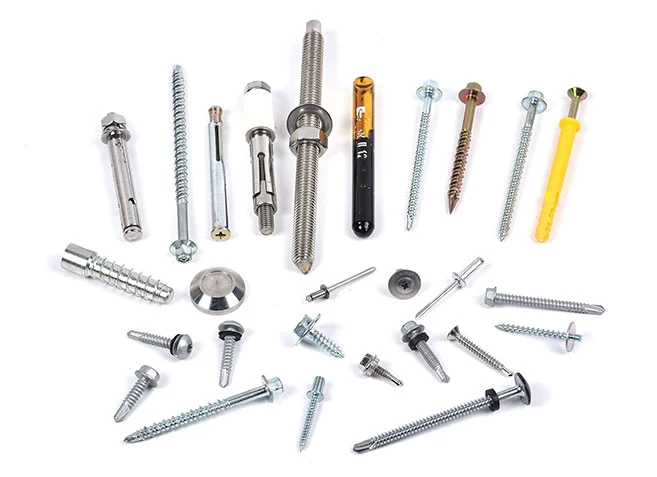 Construction Screws
Construction Screws
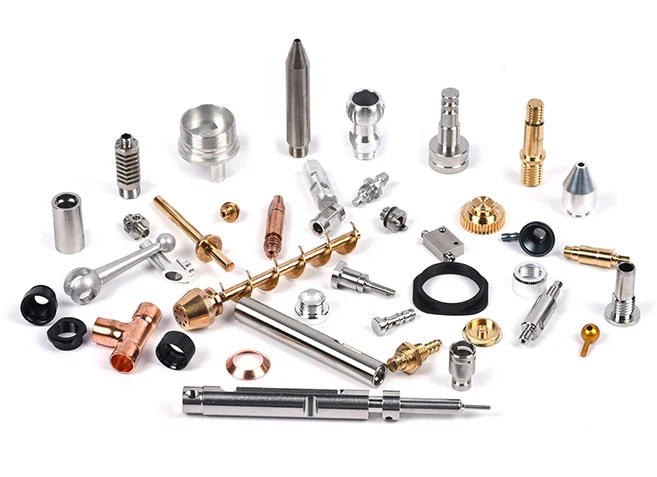 CNC Lathe Machining Parts
CNC Lathe Machining Parts
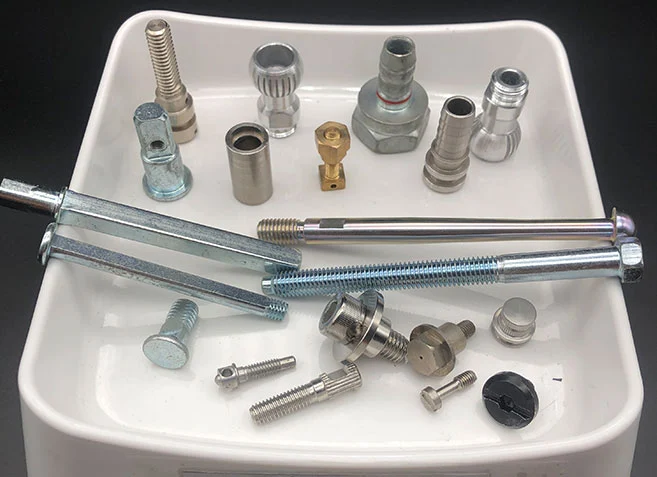 Cold Forged and Undergo Secondary Processing Products
Cold Forged and Undergo Secondary Processing Products
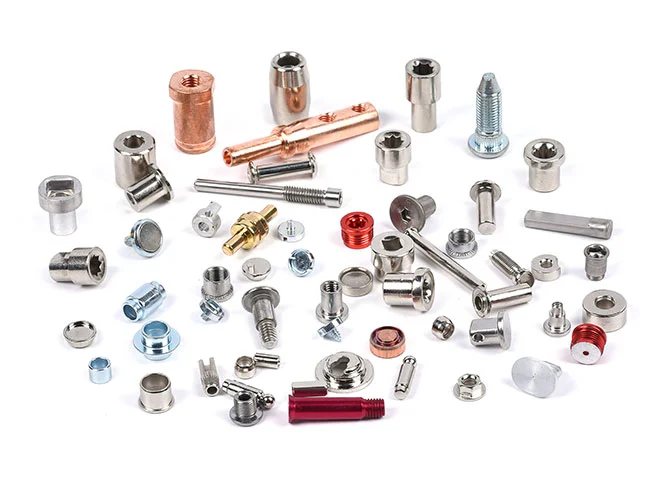 Multi Station Cold Heading Screws
Multi Station Cold Heading Screws
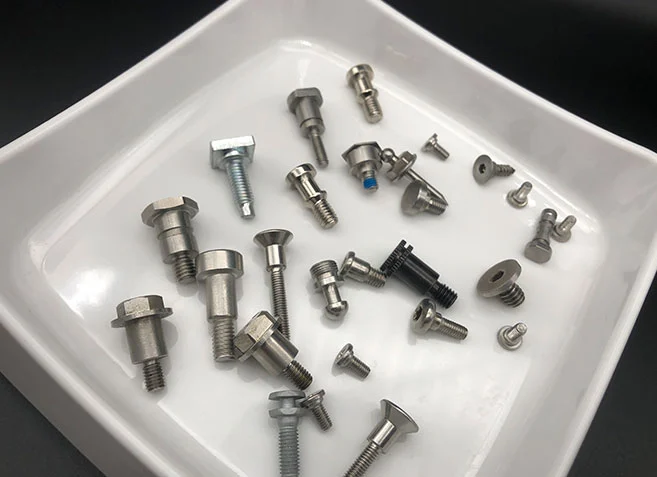 Step Screw
Step Screw
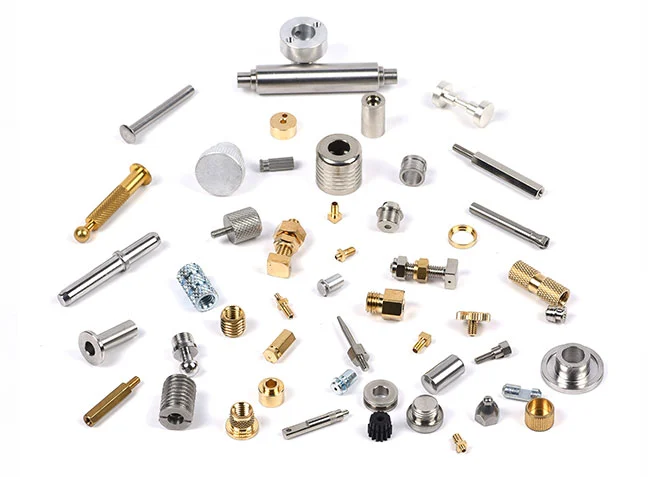 Automatic Lathe Machining Parts
Automatic Lathe Machining Parts
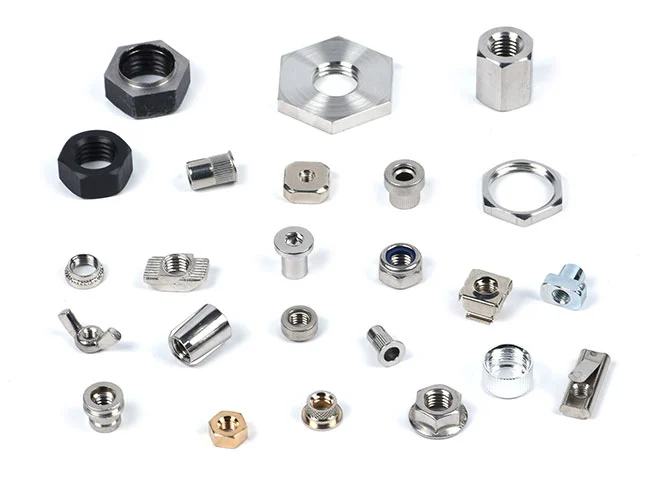 High Difficulty Challenge Cold Heading Fasteners
High Difficulty Challenge Cold Heading Fasteners
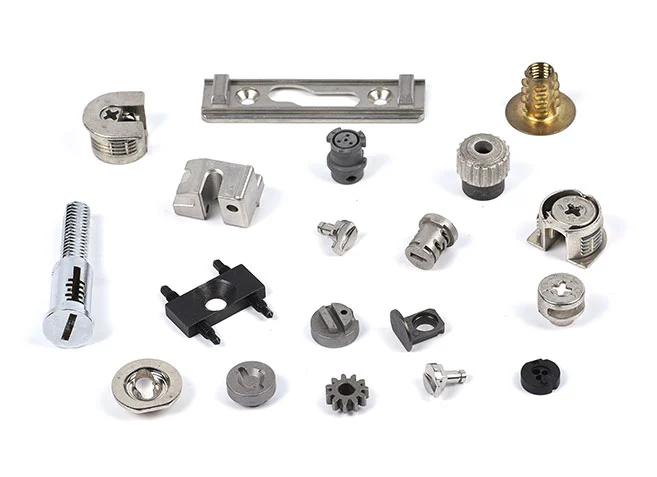 New Tech Fasteners
New Tech Fasteners
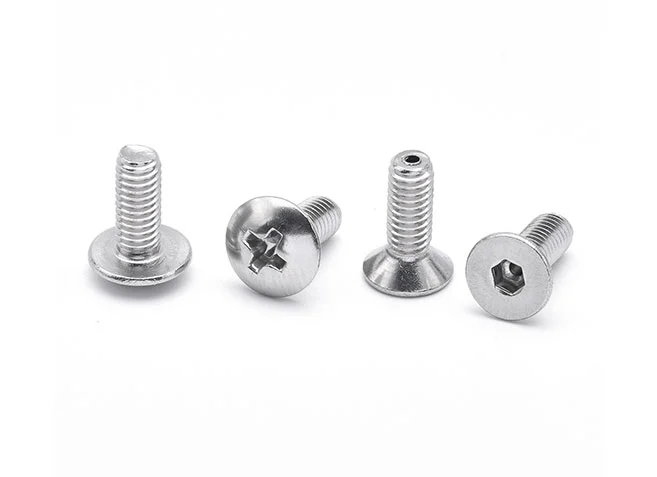 Machine Screws
Machine Screws
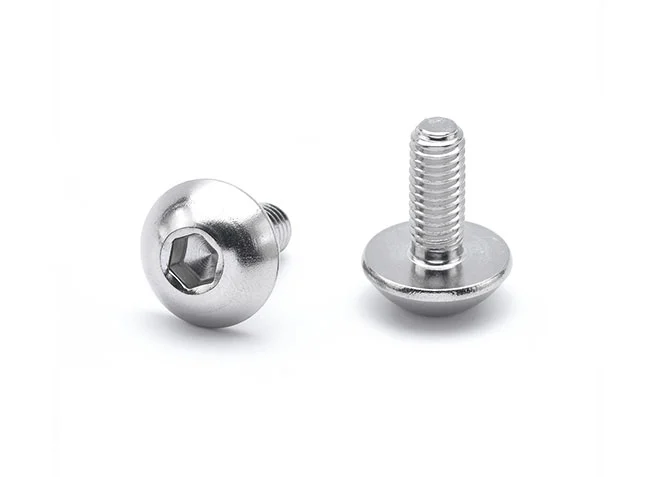 Socket Cap Screws
Socket Cap Screws
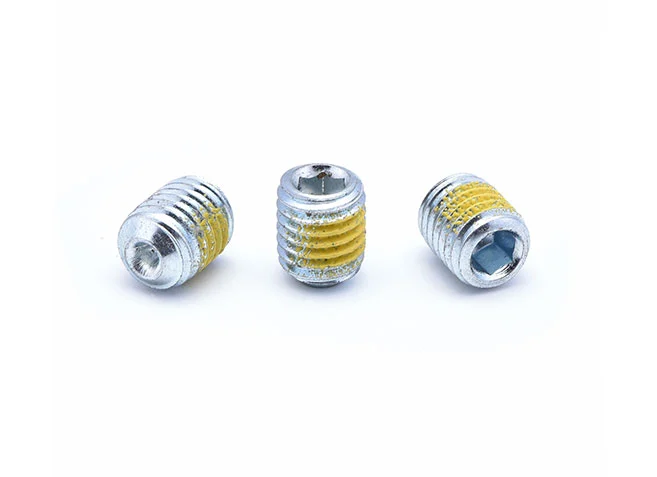 Hexagon Socket Set Screws
Hexagon Socket Set Screws
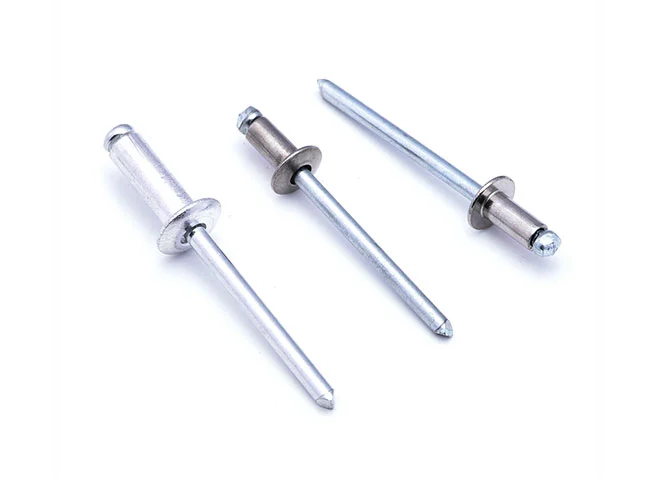 Pull Out Rivet
Pull Out Rivet
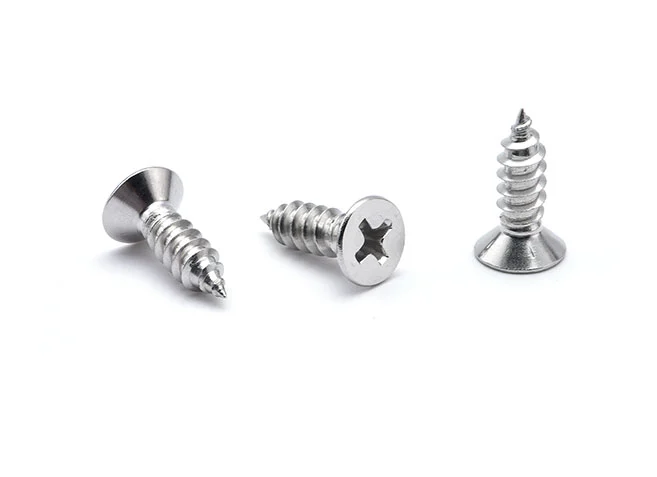 Self Tapping Screws
Self Tapping Screws
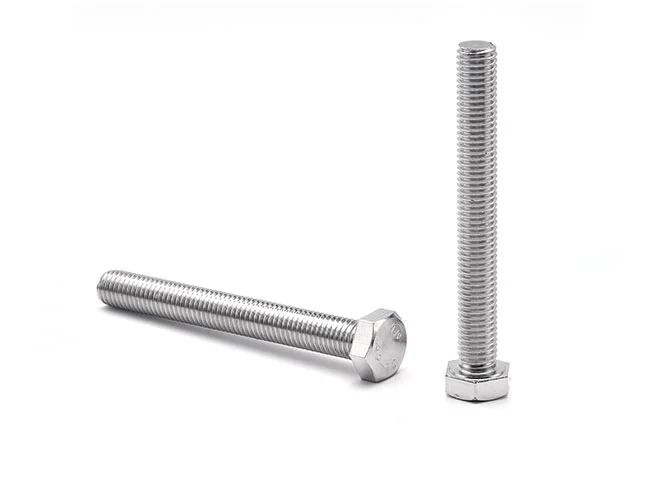 Hex Bolts
Hex Bolts
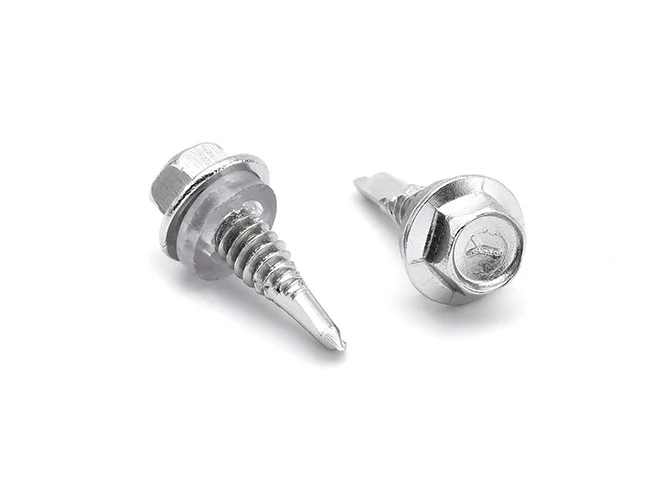 Self Drilling Screws
Self Drilling Screws
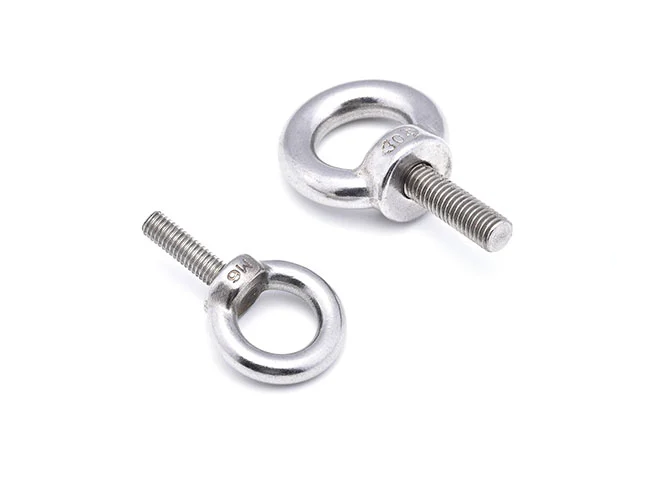 Eye Bolts
Eye Bolts
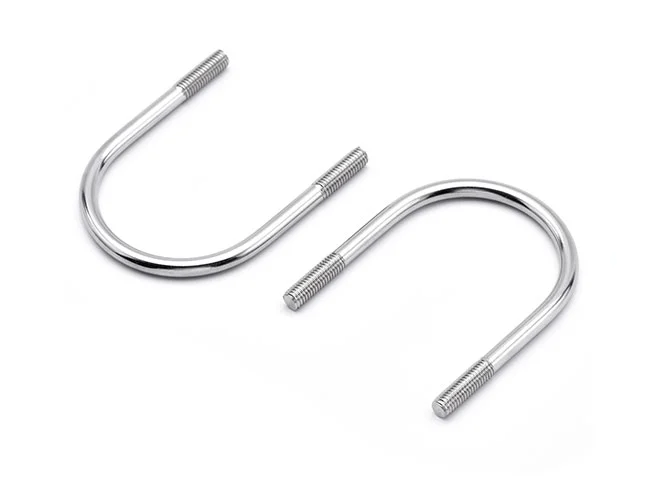 U-bolts
U-bolts
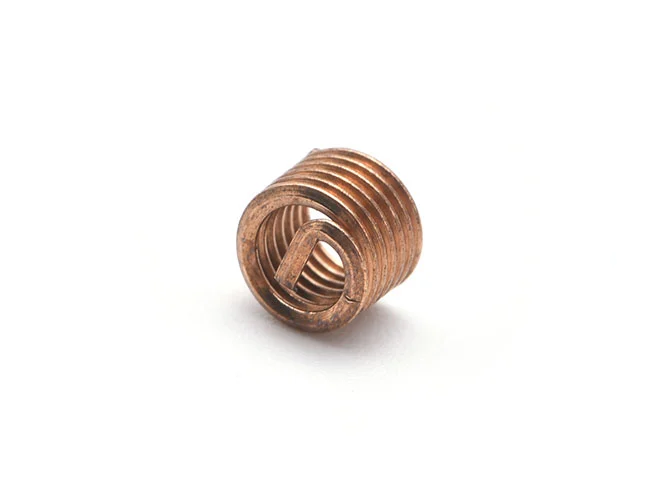 Threaded Sheath
Threaded Sheath
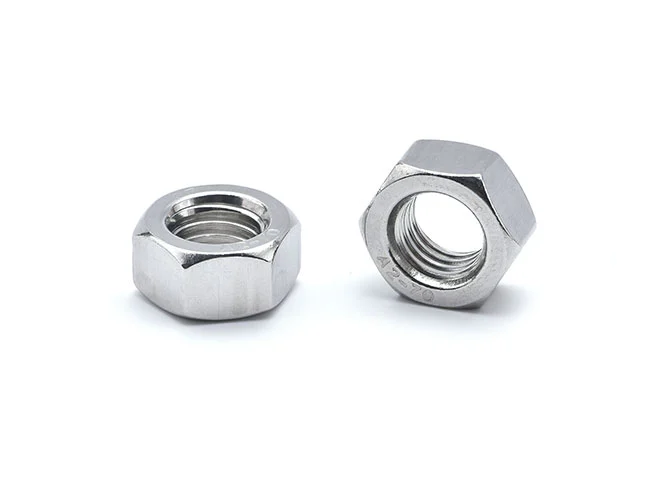 Hex Nut
Hex Nut
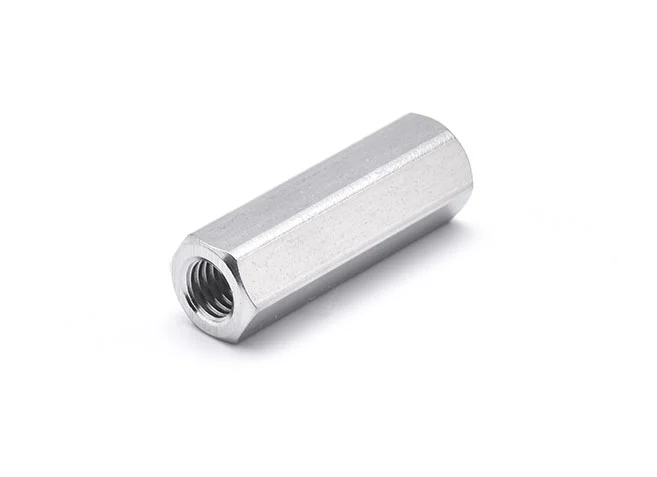 Hex Long Nut
Hex Long Nut
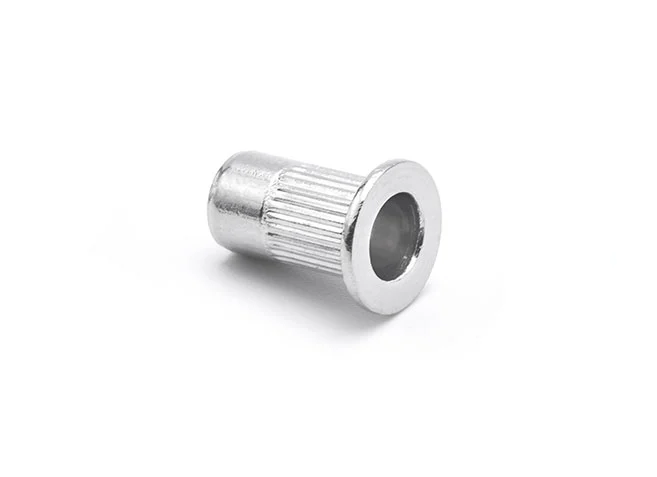 Pull Rivet Nut
Pull Rivet Nut
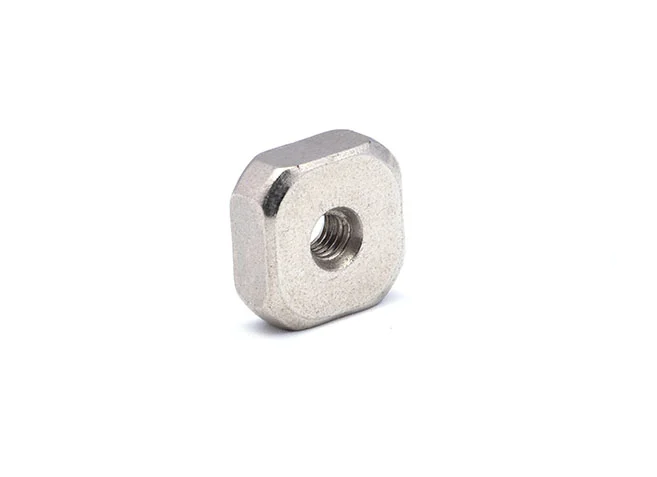 Square Nuts
Square Nuts
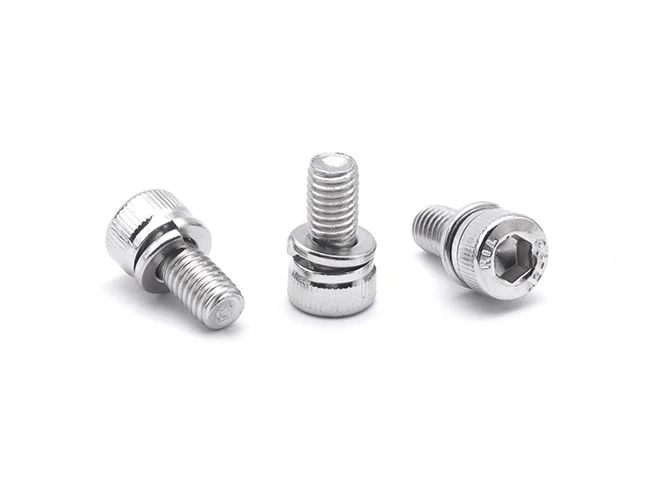 Combination Screws
Combination Screws
 Pin
Pin
 Nylon Locking Nuts
Nylon Locking Nuts
 Pressure Rivet Nuts
Pressure Rivet Nuts
 Cage Nut
Cage Nut
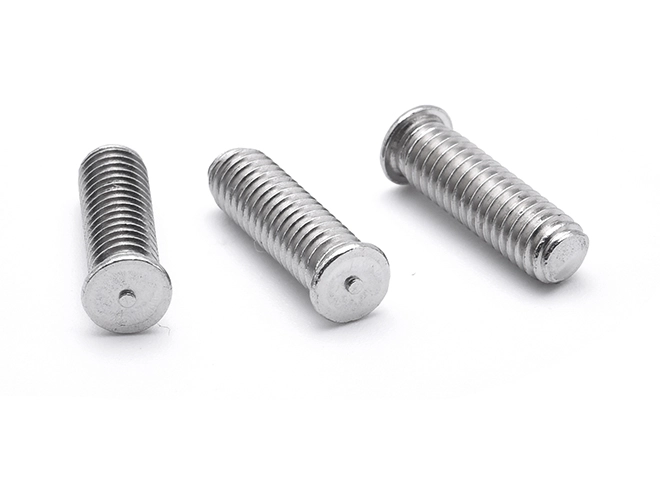 Welding Screws
Welding Screws
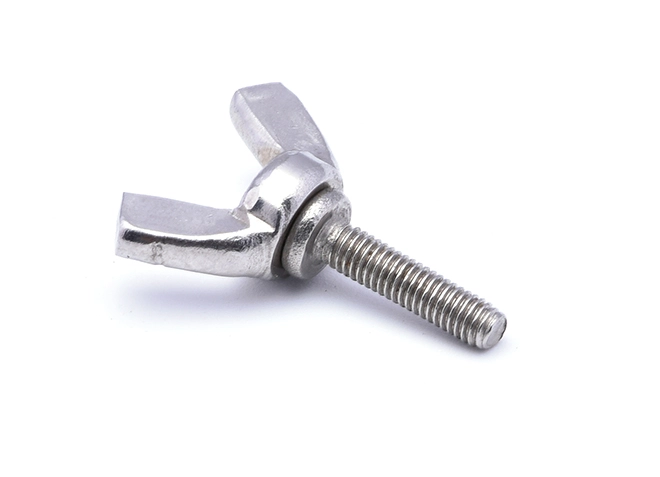 Butterfly Screw
Butterfly Screw
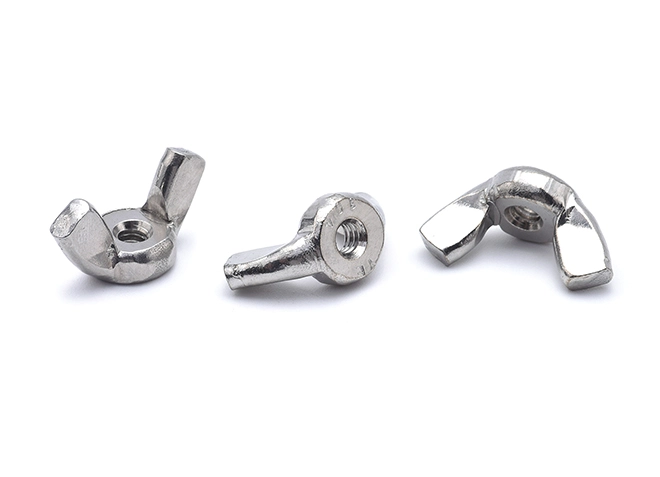 American Standard Butterfly Nut
American Standard Butterfly Nut
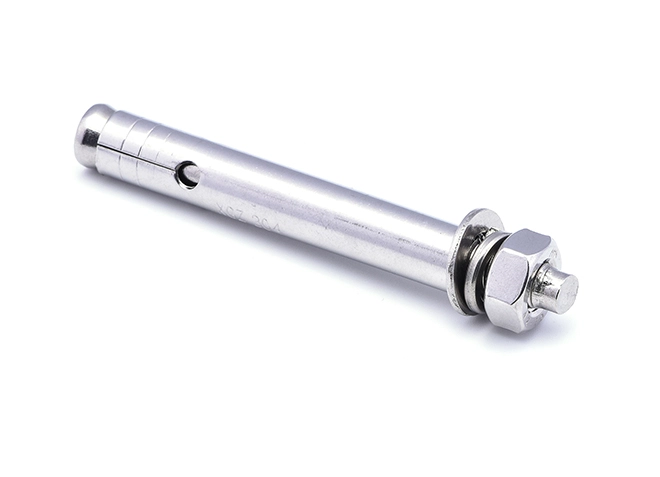 Expansion Screw
Expansion Screw
 Plug Screw
Plug Screw
 Stainless Steel Washer
Stainless Steel Washer
 Double Overlap Anti-Loosening Washers
Double Overlap Anti-Loosening Washers
 Waterproof and Anti-Drop Screws
Waterproof and Anti-Drop Screws
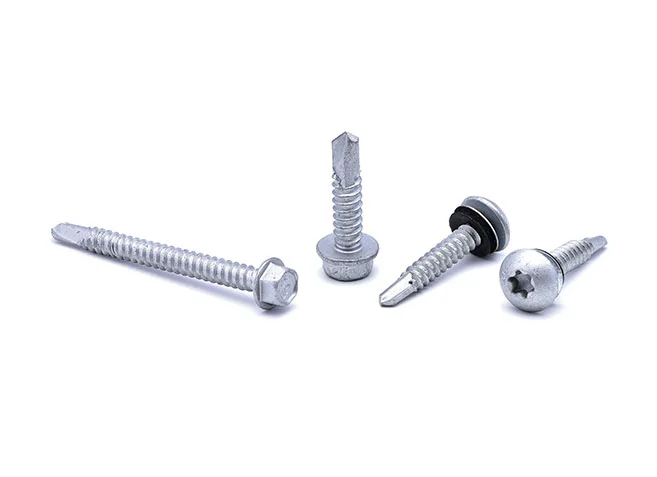 Super Corrosion-Resistant Screws
Super Corrosion-Resistant Screws
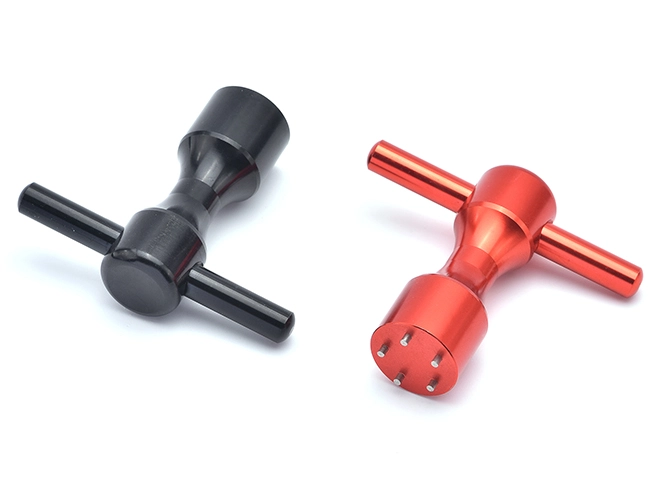 New Type Switchgear
New Type Switchgear
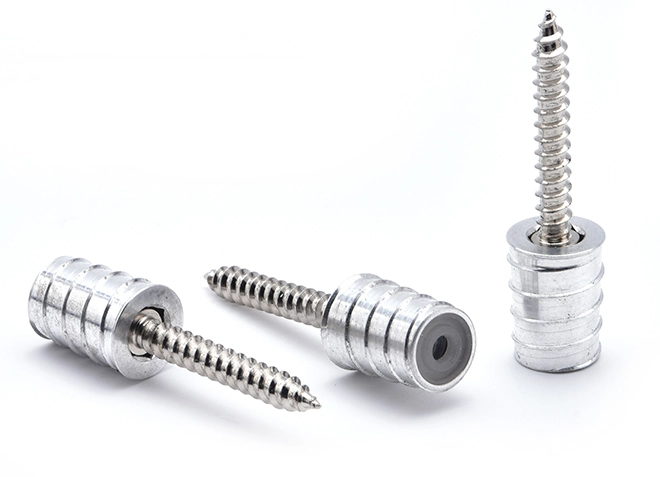 Anti-loose Easy Disassembly Nut Pillar (New Furniture Connector)
Anti-loose Easy Disassembly Nut Pillar (New Furniture Connector)
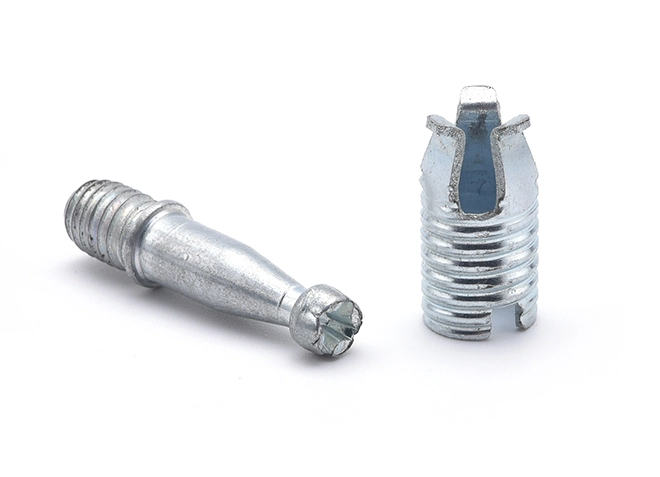 Furniture Simple Assembly and Disassembly Connector
Furniture Simple Assembly and Disassembly Connector
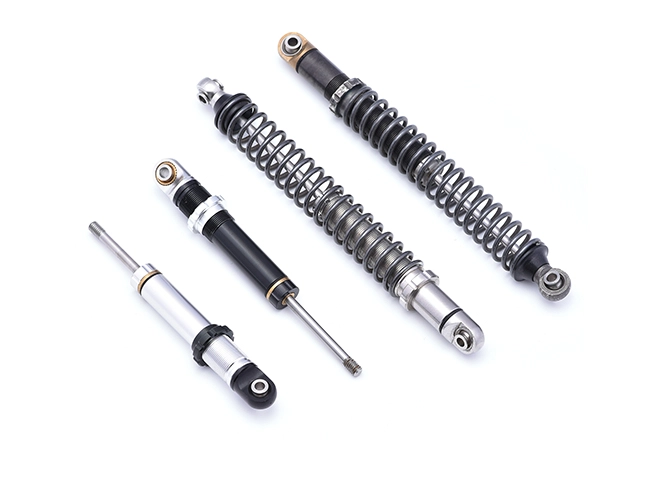 Micro Vibration Absorber
Micro Vibration Absorber
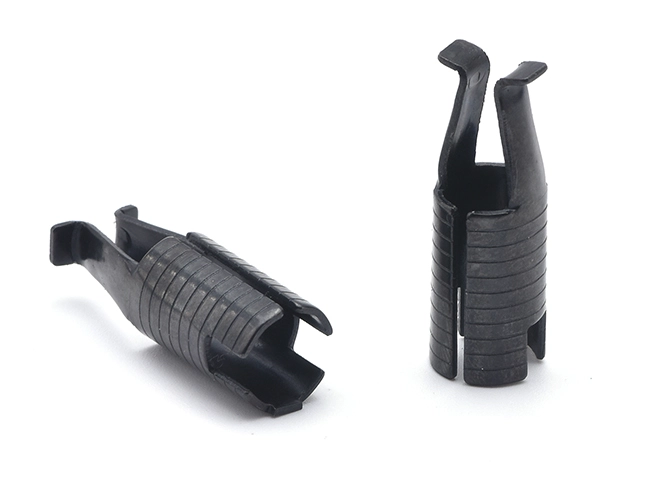 65Mn Material Furniture Connector
65Mn Material Furniture Connector
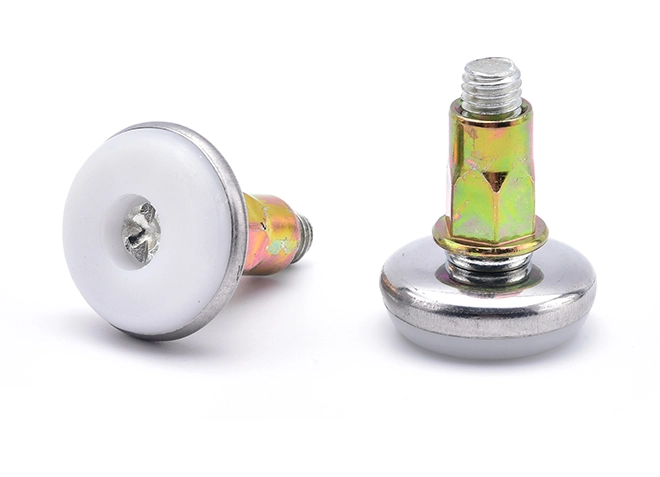 Counter Table Base
Counter Table Base
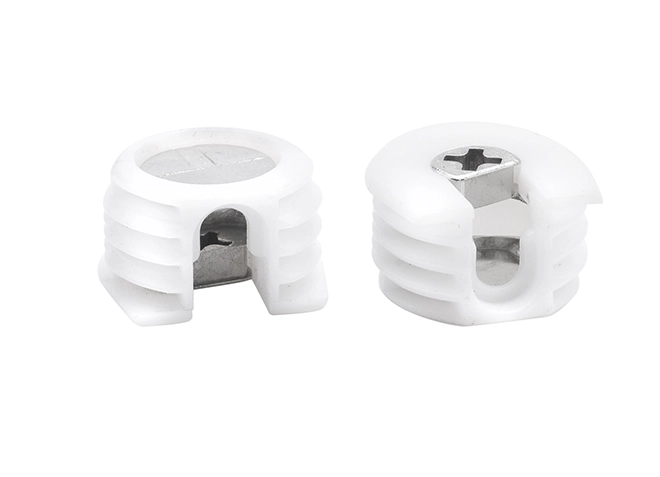 Furniture Connector Nut with Plastic Sleeve
Furniture Connector Nut with Plastic Sleeve
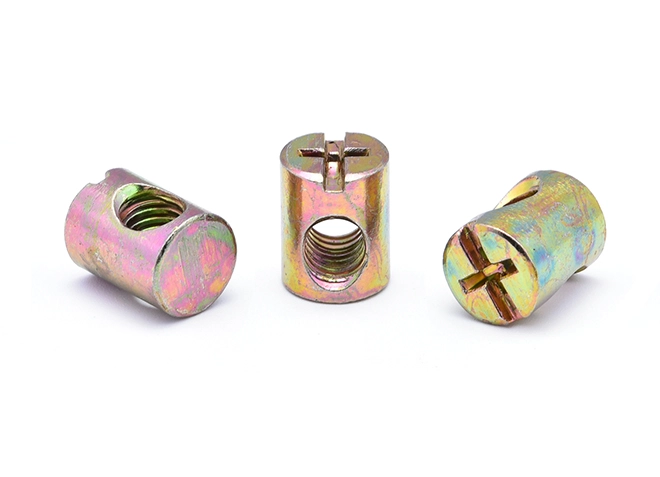 Furniture Horizontal Hole Nut
Furniture Horizontal Hole Nut
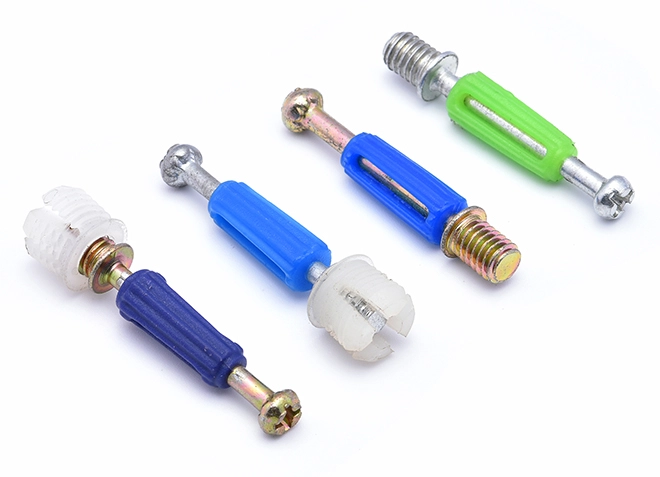 Furniture Connecting Screw
Furniture Connecting Screw
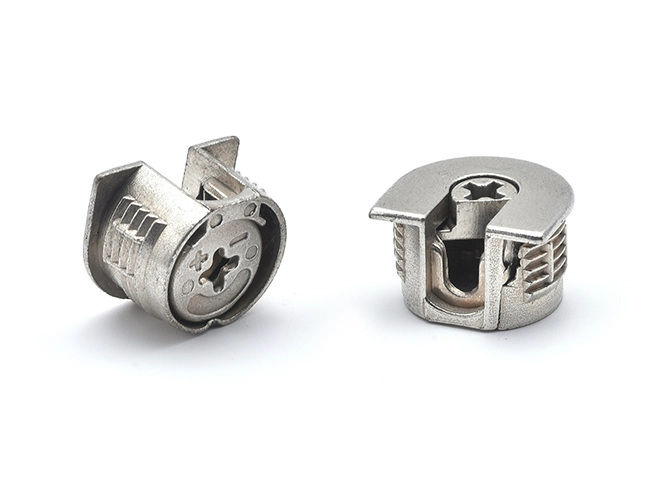 Furniture Connecting Nut Seat
Furniture Connecting Nut Seat
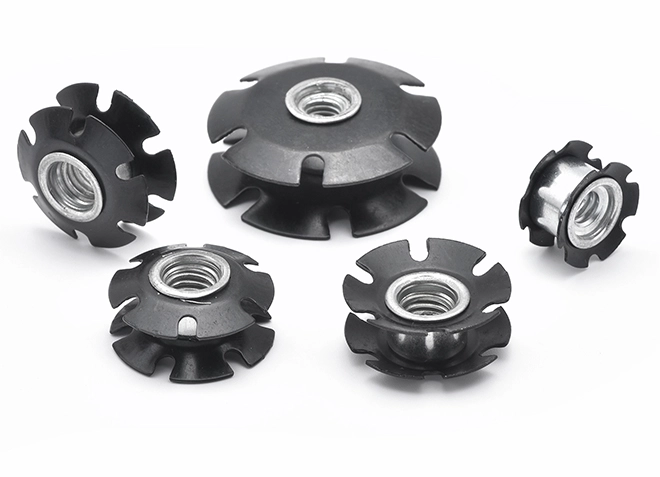 Double Stack Wheels Used On Furniture
Double Stack Wheels Used On Furniture
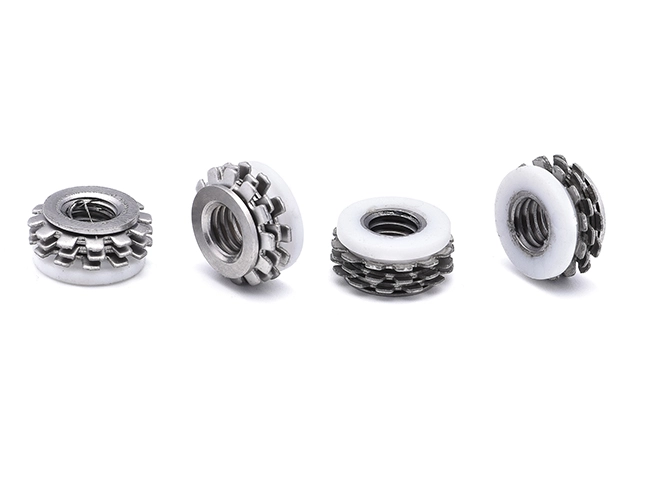 Components Used On Furniture
Components Used On Furniture
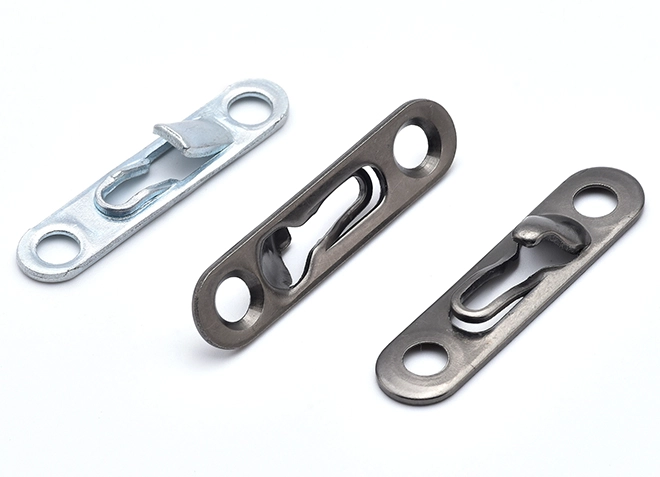 Connection Buckle
Connection Buckle
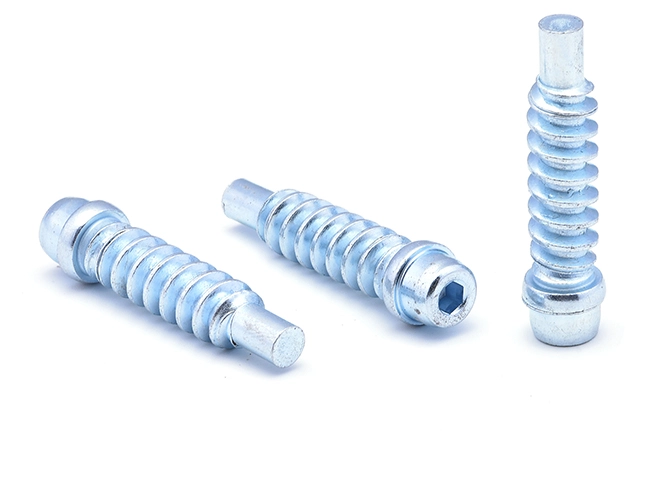 Internal Hexagonal Spiral Screw
Internal Hexagonal Spiral Screw
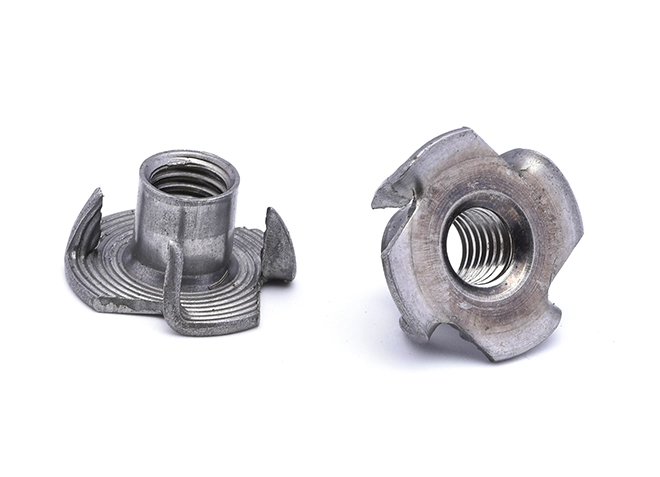 Iron Colored Carbon Steel Four Claw Nut
Iron Colored Carbon Steel Four Claw Nut
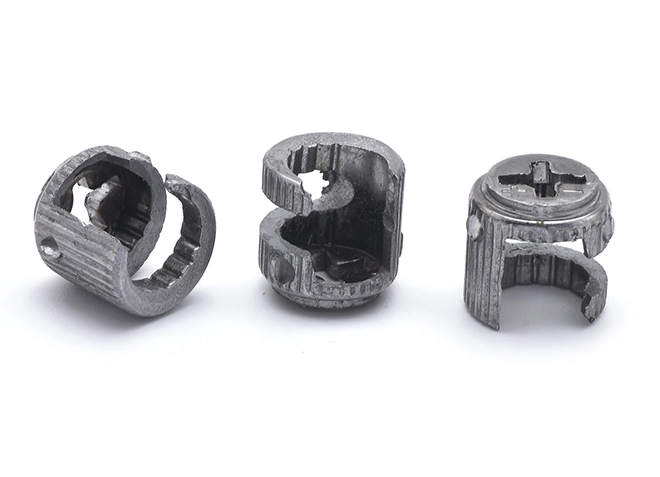 Iron Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
Iron Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
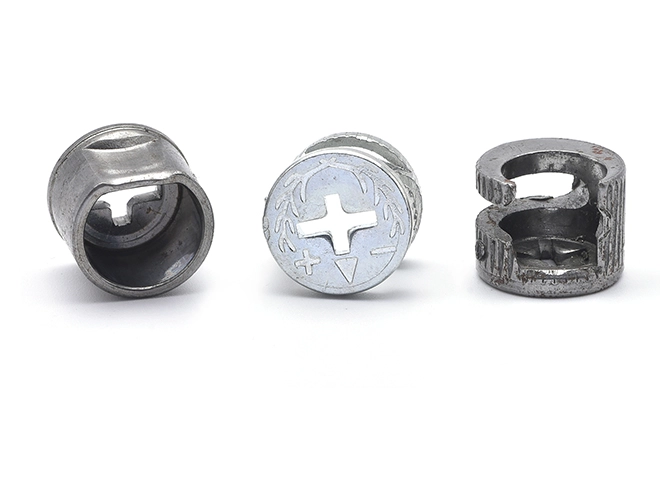 Iron and Zinc Alloy Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
Iron and Zinc Alloy Furniture Three Combination Nut Seat
 Dowel Pin+ Gray Elephant Rubber Sleeve
Dowel Pin+ Gray Elephant Rubber Sleeve
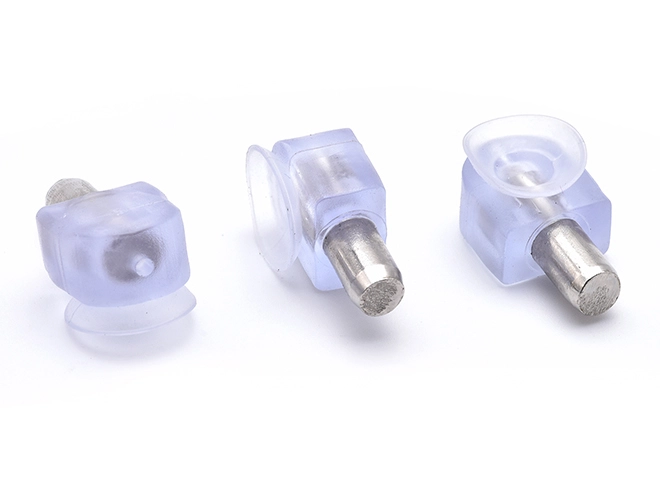 Dowel Pin+ Transparent Elephant Rubber Sleeve
Dowel Pin+ Transparent Elephant Rubber Sleeve
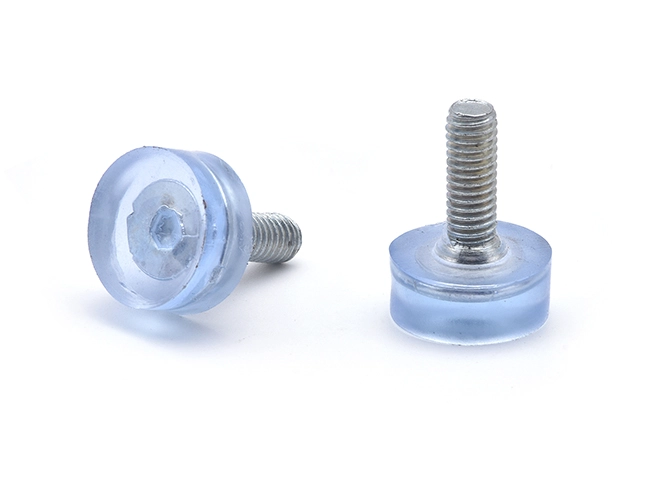 Injection Molded Furniture Foot Pad Screw
Injection Molded Furniture Foot Pad Screw



The U-shaped Screw, also known as a U-bolt, is a highly versatile and robust fastener designed to securely anchor pipes, conduits, and cables to surfaces. This screw features a U-shaped curve with threaded arms that allow it to be easily attached around the item being secured, providing a firm grip that prevents movement. Made from durable materials, the U-shaped Screw is built to withstand both mechanical stress and environmental elements, making it suitable for a wide range of applications including plumbing, electrical installations, and automotive systems. Its straightforward design ensures easy installation and adjustment.
Material and Construction: U-bolts are commonly made from steel or stainless steel. Steel U-bolts offer high strength for heavy-duty applications, while stainless steel U-bolts provide excellent corrosion resistance but may have slightly lower tensile strength.
Diameter and Thread Size: The load rating of a U-bolt increases with its diameter and thread size. Larger diameters and appropriate thread sizes can handle greater forces, but the overall strength also depends on the material used.
Load Ratings: Manufacturers provide specific load ratings for U-bolts, which can range from a few thousand pounds to over 10,000 pounds. It's essential to consult these ratings and consider safety factors to ensure the U-bolt is suitable for the intended application.
Understanding the Differences
U-bolts and J-bolts are both curved fasteners, but their designs and applications vary significantly:
| Feature | U-Bolt | J-Bolt |
Shape | U-shaped with two threaded arms | J-shaped with one threaded end |
Primary Use | Clamping pipes, cables, or round objects | Anchoring structures to concrete or masonry |
Load Direction | Radial (holds objects in place) | Axial (vertical tension resistance) |
Installation | Requires nuts on both ends | Embedded into concrete during pouring |
When to Choose a U-Bolt
Industrial Piping: Secure HVAC ducts, hydraulic lines, or exhaust systems.
Automotive: Mount leaf springs, shock absorbers, or fuel tanks.
Marine: Fasten rigging wires or deck fixtures (use 316 stainless steel for saltwater).
Example: A solar farm used galvanized U-bolts to anchor panel rails to steel beams, resisting wind loads up to 130 mph.
When to Choose a J-Bolt
Construction: Anchor steel columns to concrete foundations.
Telecom: Stabilize utility poles or antenna towers.
Safety Rails: Bolt handrails to floors in commercial buildings.
Example: A warehouse used hot-dip galvanized J-bolts to secure storage racks to concrete, supporting 10,000+ lb loads.
Decision Checklist
Load Type: Radial (U-bolt) vs. Vertical (J-bolt).
Environment: Stainless steel for corrosion; carbon steel for indoor use.
Installation Time: U-bolts are faster to retrofit; J-bolts require pre-embedding.
arron18129983931@gmail.com
arron18129983931@gmail.com
arron18129983931@gmail.com






